




Key Body Parts of Animals and Their Uses for Students
Do you know some interesting facts about animals? Hummingbirds are the only birds that fly backwards. Another one is the coconut crab which has the strongest gripping claws and the last one is Platypus turtles also have beaks but are not birds.
Animals are living organisms just like us and a part of our planet. The body parts of animals include beaks, claws, tails, legs, etc. Animals use these parts to perform multiple actions. They can use these body parts for catching prey, eating food or just for movement.
Animal Body Parts and Functions
Legs
These are very important and can vary in great numbers from one animal to another. Animals like dogs, zebras, lions etc., have 4 legs whereas spiders have 8 and some insects have 6.
The leg strength varies a lot among various animals. Cheetahs use their legs to run very fast at about 80-128 km/h. Whereas, the legs of elephants are extremely heavy and are used to crush branches and stems as they eat them.
The insect legs often have small hairy structures which allow them to walk upright on walls or any vertical surface. You must have seen spiders on ceilings and ants walking in a line on walls.
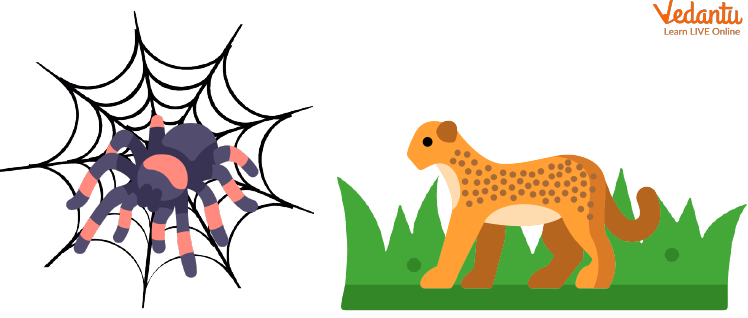
Legs of Animals
Tails
These are long muscular parts in many animals that arise from the rear part of the body, mostly the lower back.
Tails are used by land animals for balance while walking and running. They also use it to brush off flies or insects that bite them. Tails in monkeys are used to move from one tree to another and also maintain balance while jumping.
In many cases, animals have detaching tails such as lizards. It helps them to escape from the predators, when the predator gets hold of them, their tails break and allows them to escape the grasp of their predators. Some animals have sharp quills that can cause serious injury to their predators and thus can save themselves.
Some animals like rattlesnakes have tails that can make a distinct sound and keep their predators away or distract them while they escape.
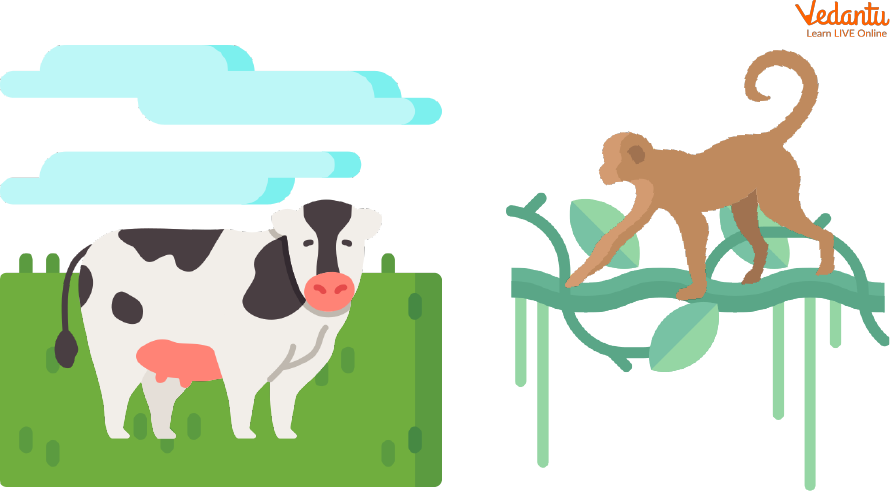
Types of Tails in Animals
Claws
Claws in animals are of immense variety among various animals. They have many uses depending on animals such as catching prey, climbing, and self-defense.
Carnivorous animals use their claws to injure their prey and slow them down to bite and kill for them to consume. They have a special type of claw that has retractable nails, i.e. the nails hide under their paws when not needed and that allows them to stay sharp and strong and not get damaged unnecessarily.
Animals like monkeys and lizards use claws to grip the surfaces they are climbing on. These claws are just like the nails that we humans have but a lot sharper and pointed allowing them to attach to tree trunks or walls.
Claws can be a useful tool for digging soil. Animals like Armadillo dig soil to find insects and fruits inside the soil. Various reptiles dig up soil to lay eggs and incubate them for them to hatch.
The right claws as seen in other animals are absent among humans as they are not needed for movement. The presence of hands that can grip anything and legs that can firmly place them on the ground allows them to move freely.
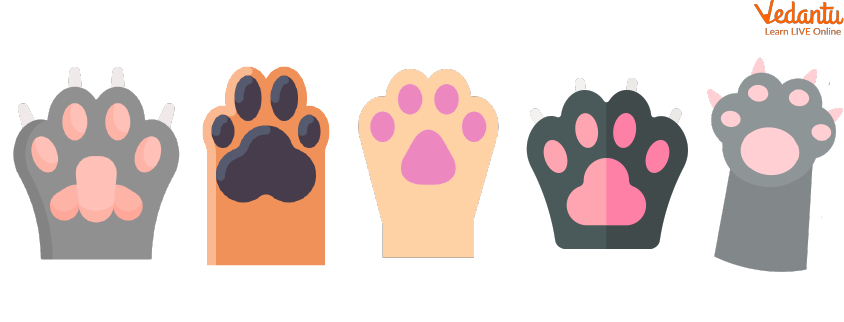
Claws
Beak
Beaks are a special mouth adaptation mostly in birds. These are of many types based on the needs of that bird.
Eagles, Hawks, and Owls generally have a hook-shaped beak that allows them to tear flesh as they are meat-eating birds. The hook acts like the canines in carnivorous animals.
Birds like canaries and sparrows have cone-shaped beaks that are useful in breaking seeds and nuts and eating their contents.
Then there are short and curved beaks which are commonly seen among parrots and macaws as they allow them to rip apart hard fruits and nuts.
Long and narrow beaks are also seen among some birds that drink nectar from flowers and juices from fruits, it also allows them to eat insects from the gaps and holes in tree trunks and flowers. e.g. Hummingbird, Robin.
There are also birds with large and heavy beaks such as pelicans and seagulls that eat fish from the sea. Their wide and strong beaks allow them to capture fish in them and not let them escape.
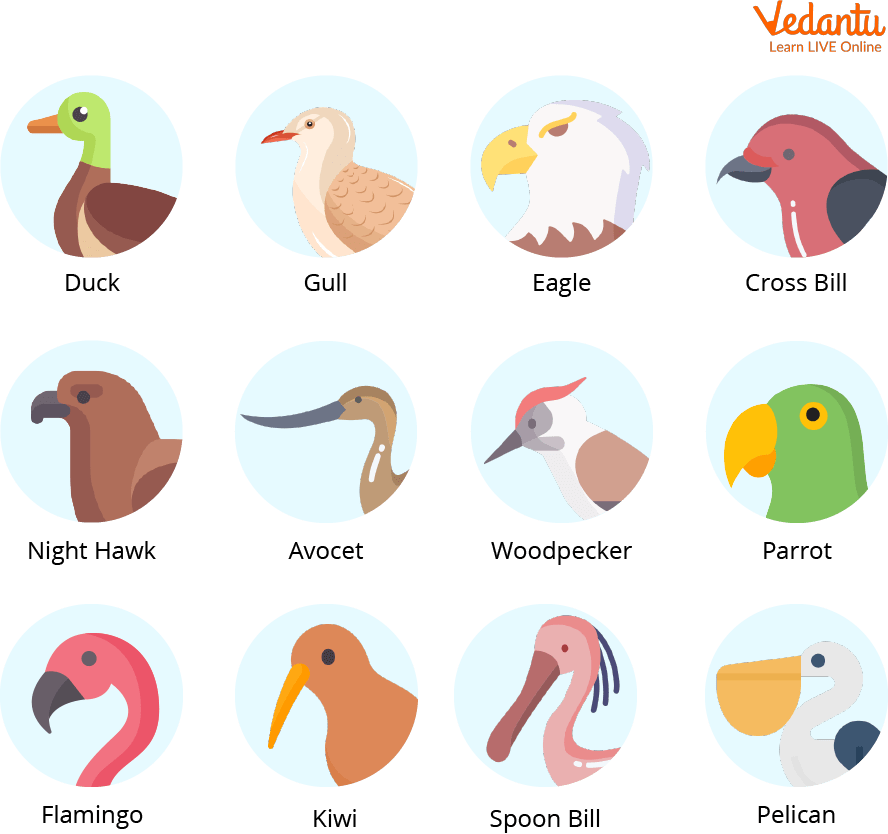
Different Types of Beaks Seen in Birds
External Parts of the Body
The external body parts of animals include the eyes, nose, mouth, legs, and tail.
These parts of the body are used as sense organs by the animals and thus are of high importance.
Most animals have a very wide vision to look out for predators in the wild.
They also showcase a very keen sense of smell allowing them to find food.
Summary
Animal body parts are of specific use against specific functions. External organs of importance change from animal to animal. Claws are an important feature in most animals. Beaks are very specific to birds and tail length varies for every other animal.
FAQs on Body Parts of Animals: Names, Functions & Pictures
1. What are the common body parts of animals and their main functions?
Animals have different body parts that help them live, move, and eat. The most common parts are:
Head: Contains the brain, eyes, ears, nose, and mouth for sensing and eating.
Torso/Body: The main part that protects important organs inside.
Limbs: These include legs for walking or running, wings for flying, or fins for swimming.
Tail: Often used for balance, communication, or swatting away insects.
2. What are the different functions of beaks in birds?
A bird's beak is a special tool that is shaped according to the food it eats. The main functions include tearing flesh in birds like eagles, cracking hard seeds in sparrows, sipping nectar from flowers in hummingbirds, and drilling into wood to find insects, as seen in woodpeckers.
3. Why do animals have so many different and special body parts?
Animals develop special body parts to help them survive in their specific environment, or habitat. These are called adaptations. For example, a fish has gills to breathe underwater, a camel has wide, padded feet to walk on hot sand, and a giraffe has a very long neck to reach leaves high up on trees. These unique parts give them an advantage in finding food and staying safe.
4. What is the importance of fur, feathers, and scales on animals?
These body coverings provide vital protection. Here’s how:
Fur: Found on mammals like bears and tigers, it helps keep them warm in cold weather.
Feathers: Found on birds, they are essential for flying, staying warm, and keeping dry.
Scales: Found on fish and reptiles, they protect the skin from injury and prevent the body from drying out.
5. How are the legs of a frog different from the legs of a horse?
The legs of a frog and a horse are different because they are adapted for different movements and environments. A horse has long, strong legs built for running fast across land. In contrast, a frog has powerful back legs designed for high jumping and webbed feet that act like paddles to help it swim efficiently in water.
6. What makes an elephant's trunk such a special body part?
An elephant's trunk is a unique and versatile body part because it functions as both a nose and a hand. An elephant uses its trunk to breathe, smell, drink water, and pick up food. It is incredibly strong, allowing it to lift heavy objects, yet it is also gentle enough to pick up something as small as a single leaf.
7. If an animal has wings, does it always mean it can fly?
No, having wings does not always mean an animal can fly. For example, the penguin has wings that it uses as flippers to 'fly' through the water with great speed, but it cannot fly in the air. Similarly, the ostrich is a large bird with wings, but it uses its powerful legs to run very fast instead of flying.
8. What are horns and antlers used for?
Horns and antlers are primarily used by animals for defence against predators and for fighting other animals, often to win a mate or territory. Horns, found on animals like sheep and cattle, are permanent and made of a bony core with a keratin sheath. Antlers, found on deer and moose, are made of pure bone and are shed and regrown each year.









