




Why Are Electronic Circuits Essential in Modern Devices?
If you are of the opinion that anything related to electronics is all technical and some sort of a code language you could never crack, you’re not completely right about it. Understanding the basics of electronic circuits like where are the various components used, how are the power sources used, different connection patterns, etc., makes the whole concept of electronics so simple.
It is important to get the foundation of electric circuits right so one can appreciate the endless possibilities it offers. In simpler words, an electronic circuit is a bigger game of connecting the dots. Let’s look at this through a bigger window.
Electronic Circuits
What is an Electronic Circuit?
An electronic circuit can be defined as a complete path through which electricity flows. It contains various components like a power source, conductors (material that allows electricity to pass through them), resistors (these are opposite of conductors), wires, and junctions. These electronic circuits having ranging complexities are used in our households and industrial setups.
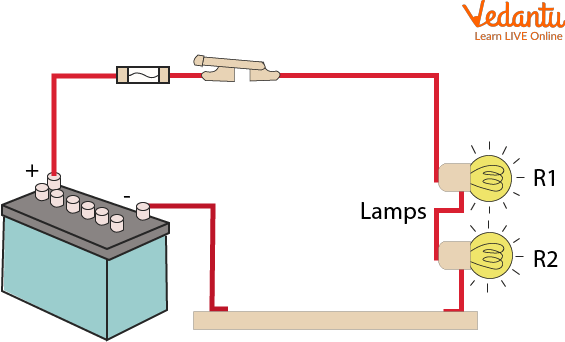
A Basic Circuit
Components of an Electronic Circuit
A basic electronic circuit consists of the following components:
A power source (cell or a group of cells called a battery)
A switch
A load (LED or resistors which consume the electricity)
Connecting wire
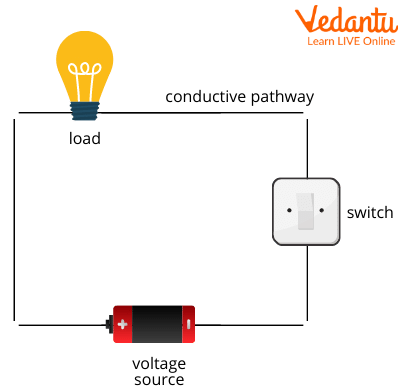
Components of an Electronic Circuit
Representation of an Electronic Circuit - Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram is a schematic representation containing various components of an electronic circuit using conventional symbols for these components. A battery has a symbol, a resistor has a symbol, and so on.

Representation of an Electronic Circuit- Circuit Diagram
Basic Components in an Electronic Circuit
Power Source:
A power source is usually a cell or a battery (a group of cells) mostly producing Direct Current (often abbreviated as DC). Alternating current (AC) is also used in electronic circuits but mostly in complex circuits.
Switch or Plug-Key:
A switch or a plug key plays an important role in ‘completing a circuit’. It is a vital component of an electronic circuit as it closes the circuit helping the flow of electricity through it.
Load:
This component consumes the power produced by the cell or battery. More often it is a LED light, a resistor, sensors, etc. They indicate the presence of current in the electronic circuit.
Connecting Wires:
These are simple wires which connect various components of the electronic circuit together.
Active and Passive Components of an Electronic Circuit
What is an Active Component?
An active component of an electronic circuit produces the electrical energy that is required for the effective functioning of the circuit. They primarily supply energy to the circuit.
A few examples of active components include:
Voltage source
Power source
Diodes (a type of energy-producing component)
Transistors (the component which multiplies produced power)
What is a Passive Component?
A passive component of an electronic circuit consumes the electrical energy that is produced by the active components for the effective functioning of the circuit. They primarily use up the energy of the circuit. Some examples of passive components include:
Resistors (components that resist the flow of electric current through them)
Capacitors (components that transiently store electric current)
Transformers (components that convert one form of current to another, AC to DC, or vice versa), etc.
Interesting Facts Related to Electronic Circuits
Electronic circuits are all based on certain basic principles and rules. Though they are of varying complexities, their basic components and functioning are pretty similar.
The current in an electronic circuit flows from the negative terminal of the cell to the positive terminal of the cell. The flow of electrons (charged species that help in the flow of electric current) is in the opposite direction of the flow of current
A switch regulates the ON and OFF of a circuit. When the switch is OFF, a gap is present in the circuit and it is considered open. Electric current cannot flow through such a circuit. The opposite process takes place if the switch is ON thus letting the flow of electric current.
The ammeter measures the current flowing through the circuit and a Voltmeter measures the voltage flowing through the circuit.
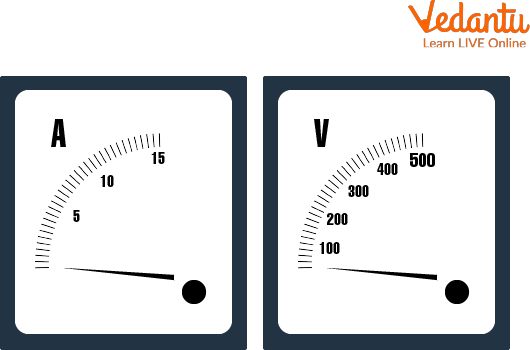
Ammeter and Voltmeter
Summary
So quickly summarising what we’ve learned up until now,
An electronic circuit is a complete and closed pathway through which electric current flows. Active and Passive components together produce an effective electric circuit. Active components produce energy that is consumed by the passive components. Active and passive components are connected by connecting wires with a switch. The switch opens or closes the circuit as per our needs. Household and industrial applications of circuits are widely varied from simple electronic circuits to complex ones
FAQs on What Is an Electronic Circuit?
1. What is an electronic circuit in simple terms?
An electronic circuit is a complete, circular path made of various electronic components through which electricity flows. For a circuit to work, it must form a closed loop, starting from a power source (like a battery), passing through components (like a light bulb or a resistor), and returning to the source. It is a specific type of electrical circuit that often includes active components that can control or manipulate the flow of electricity, such as transistors and diodes.
2. What are the three essential components of a basic electronic circuit?
Every basic electronic circuit consists of three fundamental parts:
- A Power Source: This provides the energy for the circuit, such as a battery or a power supply. It creates the voltage that pushes the electric current.
- A Conductor: These are the wires or traces that provide a path for the electric current to travel between components. Copper is a common material for conductors.
- A Load: This is the device that consumes the electrical energy and converts it into another form, such as a light bulb (producing light and heat), a motor (producing motion), or a buzzer (producing sound).
3. Can you give a simple example of an electronic circuit?
A very simple and common example of an electronic circuit is a flashlight. In a flashlight:
- The power source is the batteries.
- The conductors are the metal strips and the switch mechanism inside.
- The load is the small light bulb or LED.
4. What is the difference between an electrical circuit and an electronic circuit?
While related, the key difference is in the components and their function. An electrical circuit is any path for transmitting electric current, usually to perform a simple task like generating light or heat. An electronic circuit is a more advanced type of electrical circuit that includes active components like transistors and diodes. These components can amplify signals or perform logic operations, enabling complex functions found in computers, smartphones, and other smart devices.
5. Why must an electronic circuit be a closed loop to function?
An electronic circuit must be a closed loop because electric current needs a continuous, unbroken path to flow. Electrons leave the negative terminal of a power source, travel through the conductors and the load, and must have a path to return to the positive terminal. If there is a break anywhere in this path (known as an open circuit), the flow of electrons stops completely, and the circuit will not work. A switch is a common component used to intentionally open or close a circuit.
6. What is the difference between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)?
The primary difference between AC and DC is the direction of the current's flow.
- Direct Current (DC): The electric current flows consistently in one single direction. This is the type of power supplied by batteries, solar cells, and the power adapters used to charge electronic devices.
- Alternating Current (AC): The electric current periodically reverses its direction, flowing back and forth at a specific frequency. This is the type of power delivered to our homes and businesses through wall outlets.
7. What are the two main types of circuits based on how components are connected?
The two main configurations for connecting components in a circuit are:
- Series Circuit: In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, creating only a single path for the current to flow. A major drawback is that if one component in the series fails, the entire circuit is broken and stops working.
- Parallel Circuit: In a parallel circuit, components are connected on separate branches, providing multiple paths for the current. If one component on a branch fails, the other branches remain complete, allowing the rest of the circuit to continue functioning.
8. How are electronic circuits used in everyday household items?
Electronic circuits are the core of nearly all modern household appliances. They are found in televisions, smartphones, computers, microwave ovens, and washing machines. In each device, a specific arrangement of components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (chips) controls its functions—from changing channels on a TV to running a wash cycle or processing information on a laptop. They manage power, process signals, and execute commands to make the appliance work as intended.





















