What are the Steps and Importance of the Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle) in Photosynthesis?
The dark reaction of photosynthesis is a vital, light-independent part of photosynthesis in plants. Unlike the initial stage that needs sunlight, this phase uses energy-rich molecules from the light reaction to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. Understanding the dark reaction helps students grasp how plants manufacture food, contribute to ecosystems, and create resources essential for life on Earth.
What is the Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis?
Dark reaction of photosynthesis refers to the stage of photosynthesis where plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide into organic sugars. Also known as the light-independent or biosynthetic phase, it occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast and does not directly require light. However, it uses ATP and NADPH generated during the light-dependent reactions. The primary pathway for the dark reaction is the Calvin Cycle.
Steps of Dark Reaction: Calvin Cycle
The process mainly happens through the Calvin Cycle, which is crucial for glucose synthesis. It consists of three main stages, each catalysed by specific enzymes and requiring products from the light reaction. This cycle occurs in all green plants, algae, and some bacteria.
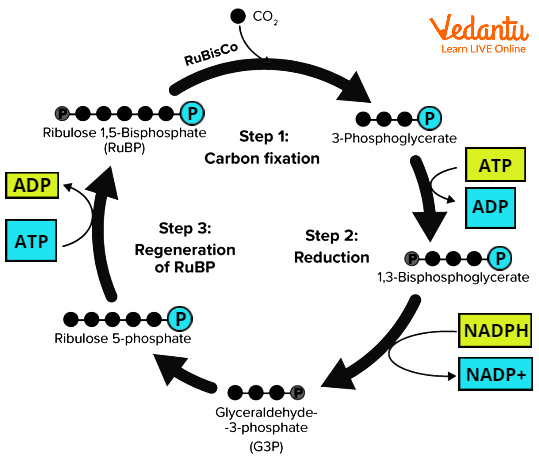
- Carboxylation: Atmospheric CO2 combines with Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO, forming two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
- Reduction: 3-PGA is converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) using energy from ATP and electrons from NADPH. Glucose is formed as carbon accumulates.
- Regeneration: Some G3P molecules regenerate RuBP, ensuring the cycle continues. This step also consumes ATP and is necessary for ongoing CO2 fixation.
The dark reaction of photosynthesis definition often highlights these sequential steps, forming the core of biology notes and class 12 curriculum.
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis Equation
The overall equation for the dark reaction (Calvin Cycle) can be represented as:
6 CO2 + 18 ATP + 12 NADPH + 12 H2O → C6H12O6 + 18 ADP + 18 Pi + 12 NADP+ + 6 H+ + 12 NADP+
This equation shows how carbon dioxide is converted into glucose using the chemical energy carriers ATP and NADPH. For more on plant biomolecules, visit biomolecules in living organisms.
Other Pathways: C4 and CAM Cycles
While the Calvin cycle is universal, some plants use alternative pathways to reduce photorespiration or adapt to dry conditions. These differences are important in agricultural and environmental biology.
Hatch and Slack Pathway (C4 Cycle)
C4 plants, such as maize or sugarcane, first fix CO2 into a four-carbon compound using phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) and the enzyme PEP carboxylase. This process occurs in mesophyll cells before entering the Calvin Cycle in bundle sheath cells, which minimizes photorespiration.
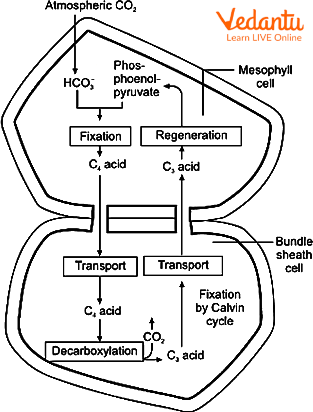
- Primary CO2 acceptor: PEP in mesophyll cells
- ATP Consumption: C4 pathway utilizes 5 ATP per CO2 fixed (2 in C4, 3 in Calvin Cycle)
- Advantage: Highly efficient even under dry or hot conditions
CAM Cycle (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism)
CAM plants, such as cacti and pineapple, have adapted to arid climates. They open their stomata at night, fixing CO2 into malate (an acid), which is stored for daytime use when the Calvin Cycle operates. This conserves water and reduces photorespiration.
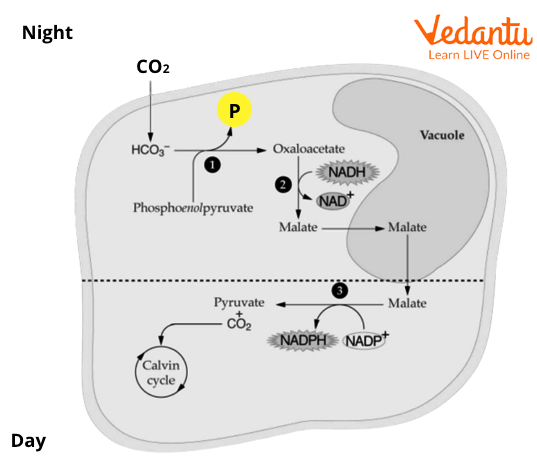
- Night: Stomata open, CO2 fixed into organic acids
- Day: Stomata close, organic acids release CO2 for the Calvin Cycle
- Real-life example: Pineapple and other succulents
For more on plant adaptations and survival strategies, explore adaptations in plants and animals.
Mechanism of Dark Reaction: Enzymes and Regulation
The dark reaction relies on a set of enzymes, with RuBisCO being the most significant as the main CO2 fixing enzyme. ATP and NADPH produced by the light reaction provide the energy and reducing power for these chemical transformations. If any step stalls, especially the regeneration of RuBP, the entire process stops. Efficient regulation ensures the plant maintains balance between energy production and glucose synthesis.
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis: Key Facts and Importance
Dark reaction of photosynthesis answers the most critical question: how do plants convert atmospheric CO2 into food? This process:
- Creates glucose, essential for plant and animal nutrition
- Helps maintain air quality by reducing CO2 levels
- Is vital for crop yields, food science, and environmental sustainability
Professionals in medicine, agriculture, and environmental science use this knowledge to improve crop efficiency and counteract climate change. For real-world applications, explore food science and effects of climate change on crops.
Difference Between Light and Dark Reaction
| Light Reaction | Dark Reaction |
|---|---|
| Occurs in the thylakoid membrane and depends on sunlight | Occurs in the stroma and does not directly require light |
| Produces ATP and NADPH | Uses ATP and NADPH for CO2 fixation |
| Oxygen is released | Glucose is formed; CO2 is used |
| Chlorophyll and photosystems involved | Enzymes like RuBisCO involved, no photosystems |
Understanding these differences is important for concepts like cellular respiration and photosynthesis, as seen in differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Examples and Applications of Dark Reaction
Some dark reaction of photosynthesis examples include:
- Leaf cells in wheat (C3 plant) conducting the Calvin cycle all day
- Sugarcane leaves displaying both C4 and Calvin Cycle for efficient sugar production
- Pineapple plants using the CAM cycle to conserve water while making glucose
These biological processes influence food chains, oxygen production, medicine (like drugs derived from plants), and environmental stability. Visit food and health for more real-world relevance.
Practice Questions: Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis
- What are the final products of the dark reaction?
- Write and explain the balanced equation for the Calvin Cycle.
- How do CAM plants minimize water loss during photosynthesis?
- Differentiate between C3 and C4 pathways in terms of ATP use and adaptation.
For more practice and MCQs, explore biology MCQs on Vedantu.
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis: Short Notes
- Occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts
- Does not directly require sunlight
- Main enzyme: RuBisCO
- Main product: Glucose
- Involves Calvin, C4, and CAM cycles
For quick revision notes and diagrams, refer to photosynthesis process on Vedantu.
Page Summary
The dark reaction of photosynthesis is a key process where plants use ATP and NADPH from the light reaction to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. Understanding its mechanisms, pathways, and significance is vital for biology, agriculture, and environmental science. Vedantu provides detailed notes, examples, and diagrams to help students master this essential topic.


FAQs on Understanding the Dark Reaction Of Photosynthesis
1. What is the dark reaction of photosynthesis?
The dark reaction of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle or C3 cycle, is the stage where plants convert carbon dioxide into glucose without requiring light.
Key features:
- Occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts
- Does not need direct sunlight (but depends on products from the light reaction)
- Uses ATP and NADPH generated during the light reaction
- Incorporates CO₂ into glucose via the Calvin cycle
2. Where does the dark reaction take place in a plant cell?
The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast in plant cells.
- The stroma is the fluid-filled space outside the thylakoid membranes
- It contains enzymes required for the Calvin cycle
- All carbon fixation steps of photosynthesis happen here
3. What are the main steps of the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis?
The Calvin cycle consists of three primary steps that fix carbon and produce glucose.
Main steps:
- Carbon fixation: CO₂ attaches to RuBP with help from the enzyme Rubisco
- Reduction: ATP and NADPH convert 3-PGA into G3P (a sugar molecule)
- Regeneration: Some G3P regenerate RuBP so the cycle can continue
4. Why is the dark reaction called the light-independent reaction?
The dark reaction is called light-independent because it does not require light directly, though it relies on energy carriers produced in the light reaction.
- Uses ATP and NADPH made in the light reaction
- Can happen both day and night if these products are available
- Performs carbon fixation to produce glucose
5. What is the role of ATP and NADPH in the dark reaction?
ATP and NADPH act as energy carriers and reducing agents in the dark reaction.
- ATP provides energy for the biosynthetic processes of the Calvin cycle
- NADPH supplies electrons needed to convert 3-PGA into G3P
- Both are generated in the light reaction and consumed in the dark reaction
6. What are the products of the dark reaction in photosynthesis?
The main product of the dark reaction is glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), along with other sugars and compounds needed by the plant.
- Glucose is synthesized from CO₂
- Partially formed sugars like G3P (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate) are also produced
- These chemicals are used for energy, growth, and storing as starch
7. What is the difference between the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis?
The light reaction and dark reaction differ in their requirements and outcomes in photosynthesis.
- Light reaction requires sunlight and occurs in thylakoids; produces ATP, NADPH, O₂
- Dark reaction does not require light; happens in stroma; uses ATP and NADPH to fix CO₂ into glucose
- Both reactions are interdependent and essential for photosynthesis
8. Which enzyme is crucial for the dark reaction of photosynthesis?
Rubisco is the key enzyme regulating the dark reaction in photosynthesis.
- Full name: Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
- Facilitates the fixation of CO₂ onto RuBP
- Exists abundantly in the chloroplast stroma
9. Why is the dark reaction important for plants?
The dark reaction is essential as it produces the glucose needed for plant growth and energy.
- Converts CO₂ into energy-rich sugars
- Supports biosynthesis of starch, cellulose, and other macromolecules
- Enables plants to store energy and grow, even when light is not available
10. Can the dark reaction of photosynthesis occur at night?
The dark reaction can occur at night if ATP and NADPH from the light reaction are available.
- Requires products (ATP, NADPH) generated during daytime
- Does not directly depend on sunlight
- Continues until stored energy carriers are depleted
11. What is the significance of the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis?
The Calvin cycle, as part of the dark reaction, is vital for synthesizing sugars required for plant metabolism.
- Assimilates CO₂ into organic compounds like sugars
- Supplies energy and carbon skeletons for growth
- Links the light and dark phases of photosynthesis
12. List the main differences between C3 and C4 plants in terms of dark reaction.
C3 and C4 plants differ in how and where they perform the dark reaction.
- C3 plants: Use only the Calvin cycle in the stroma
- C4 plants: Use Hatch-Slack pathway (initial carbon fixation in mesophyll), followed by Calvin cycle in bundle sheath cells
- C4 pathway is more efficient under high light and temperature










