What Are the Four Types of Animal Tissue and Their Functions?
All animals, from tiny insects to large mammals, are made up of four main types of animal tissue. These tissues form the foundation of body structures and play unique roles, such as protection, movement, support, and control of body functions. Understanding the types of animal tissue helps us appreciate how our bodies grow, function, and adapt in daily life.
Types of Animal Tissue: Definition and Importance
Types of animal tissue refers to the four major categories of tissues found in animals: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. Each type of animal tissue contains specialized cells that perform specific roles essential for animal growth, protection, and response. The study of these tissues is fundamental to biology, medicine, and health sciences. Knowing how tissues work helps doctors diagnose diseases, supports medical research, and guides innovations such as tissue engineering and regenerative therapies. You can explore more about muscular tissue and its importance in animal movement via Vedantu's advanced resources.
Major Types of Animal Tissue
In multicellular animals, tissues group together to form organs that carry out life processes like digestion, sensation, and movement. The main types of animal tissue are:
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
Let's explore each type with definitions and examples:
1. Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue covers the body's surfaces, both inside and out. It lines organs, forms glands, and serves as the first defense against infections. Epithelial cells are tightly packed with minimal spaces between them, creating barriers for protection and selective absorption. This tissue rests on a thin basement membrane and lacks its own blood vessels, depending on underlying tissues for nutrients.
Types of Epithelial Tissue
- Squamous Epithelium: Flat, thin cells found in places like blood vessel walls and lung alveoli; allows for easy diffusion and filtration.
- Cuboidal Epithelium: Cube-shaped cells, present in kidney tubules and glandular ducts; involved in secretion and absorption.
- Columnar Epithelium: Tall, pillar-like cells lining the intestine and respiratory tract, vital for absorbing nutrients and secreting mucus.
- Ciliated Epithelium: Columnar cells with hair-like cilia; seen in the airways and reproductive tract, moving mucus or eggs along surfaces.
- Glandular Epithelium: Specialized for secretion; forms glands releasing hormones, enzymes, or sweat.
Examples include the skin's surface, inner lining of the mouth, the walls of alveoli, and the lining of blood vessels. Diseases like dysentery often begin when harmful agents breach epithelial tissue and enter the body, as explained in our Vedantu biology pages.
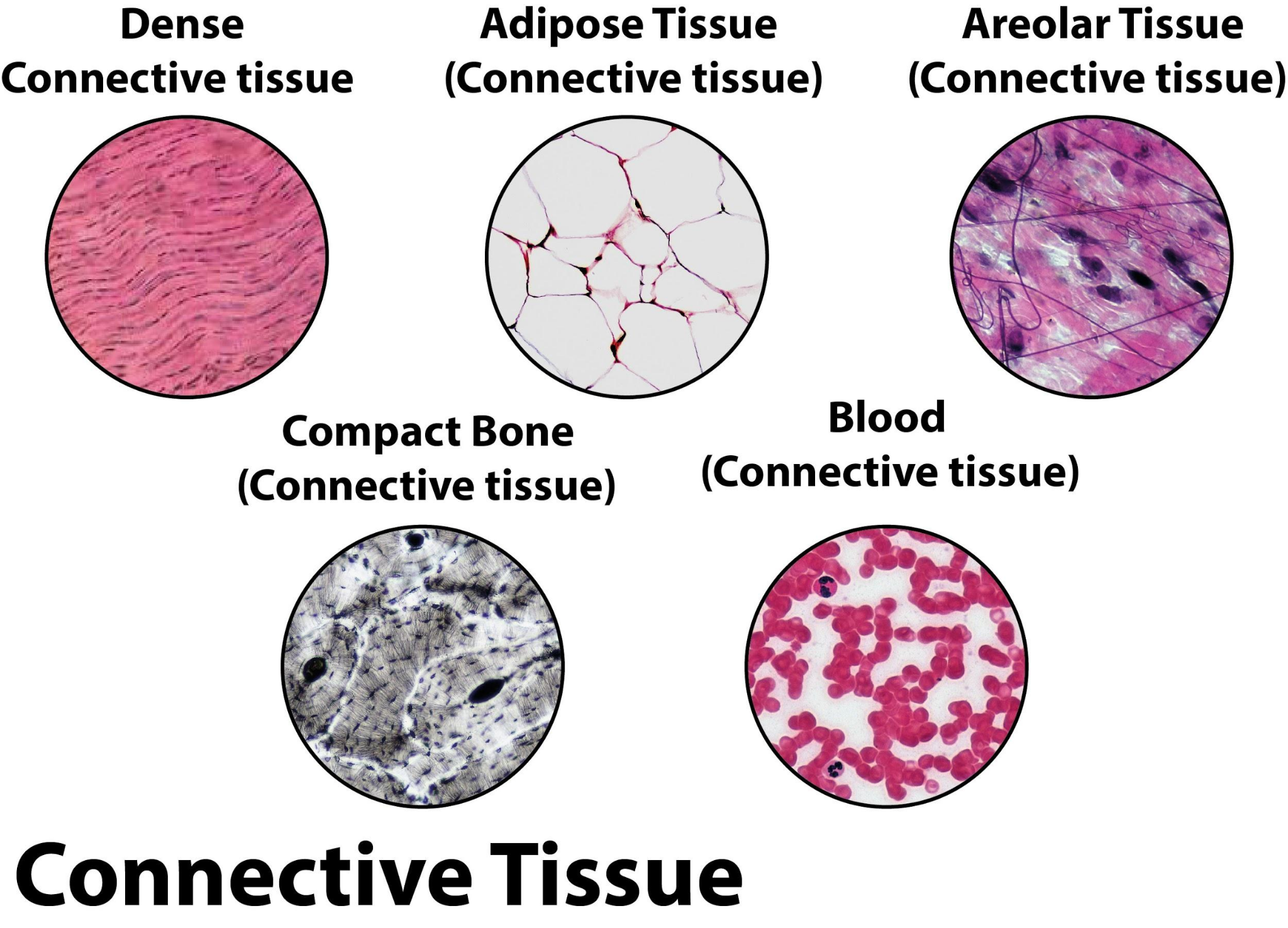
2. Connective Tissue
Connective tissue supports and connects other tissues and organs in the body. Unlike epithelial tissue, its cells are scattered within an abundant extracellular matrix made of fibers and ground substance. This flexible arrangement gives structural and metabolic support and protection.
- Examples: Bone (rigid support), blood (transports nutrients/gases), cartilage (smoothens joints), tendons and ligaments (connect muscles and bones), adipose tissue (stores fat).
Connective tissues play key roles in healing, protection, and immunity. Explore more about the difference between tendons and ligaments and their structure on Vedantu.
3. Muscular Tissue
Muscular tissue enables body movements. It consists of elongated cells, called muscle fibers, that contract and relax. There are three major types of muscular tissue:
- Skeletal Muscle: Attached to bones; responsible for voluntary movement.
- Smooth Muscle: In walls of internal organs like stomach and blood vessels; manages involuntary movements.
- Cardiac Muscle: Found only in the heart; contracts rhythmically to pump blood.
You can dive deeper into muscular tissue types and their functions for a detailed summary on Vedantu.
4. Nervous Tissue
The nervous tissue controls and coordinates body activities by transmitting electrical signals. Its main cells are neurons, which receive and send messages, and neuroglia, which support and protect neurons. Nervous tissue forms the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, allowing animals to sense changes and respond quickly.
- Examples: Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves.
Understanding nervous tissue is crucial for medical science, as it illuminates how we perceive our environment and how conditions like nerve gas poisoning affect function. Visit Parts of the Brain to learn about nerve tissue in detail.
Types of Animal Tissue Table for Quick Reference
| Type of Animal Tissue | Main Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Epithelial | Protection, absorption, secretion | Skin, lung alveoli, glands |
| Connective | Support, transport, storage | Bone, blood, cartilage, fat |
| Muscular | Movement | Arm/leg muscles, heart, intestine walls |
| Nervous | Control, coordination, response | Brain, nerves, spinal cord |
This table summarizes the types of animal tissue with their main functions and classic examples for a quick overview. Refer back whenever reviewing related biology concepts or solving types of animal tissue MCQs.
Types of Animal Tissue: Explanation with Examples
The types of animal tissue each serve special purposes:
- Protective barrier: Epithelial tissue resists germs and injury.
- Structural support: Connective tissues form everything from bone to blood, essential for body shape and energy storage.
- Movement: Muscular tissue creates all voluntary and involuntary movements, from walking to heartbeats.
- Rapid communication: Nervous tissue lets animals react swiftly, whether escaping predators or thinking deeply.
For instance, lung alveoli consist of squamous epithelial tissue to enable efficient gas exchange. Similarly, the heart combines cardiac muscle tissue with connective support. These real-life examples help you understand tissue functions when reviewing human skeletal system details or studying for animal tissue questions.
Types of Animal Tissue Diagram
A typical types of animal tissue diagram in class 12 illustrates the arrangement and structure of each tissue type within organs. Visual aids help reinforce understanding and allow quick identification during biology exams or in practical lab sessions. Students are encouraged to practice labeling these diagrams, a key part of Vedantu's biology resources.
Applications and MCQs of Animal Tissues
Knowledge of animal tissues is essential in medicine, veterinary sciences, and agriculture. It is the basis for surgical procedures, biomedical research, and treatment of diseases affecting tissues like cancer and arthritis. If you want to test your knowledge, explore types of animal tissue MCQs for exam practice or create a types of animal tissue PPT for peer presentations. Understanding tissues also aids in appreciating food value (see What do various nutrients do for our body) and environmental adaptation (animal adaptations).
Summary: Types of Animal Tissue
The four types of animal tissue—epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous—each play vital roles in an animal’s body. Understanding their structure, functions, and examples prepares students for deeper studies in biology, medical sciences, and environmental adaptation. For more concept clarity, Vedantu provides expert-led assignments, diagrams, and learning tools for all biology topics.


FAQs on Types Of Animal Tissue: Definition, Structure, and Examples
1. What are the four types of animal tissue?
The four main types of animal tissue are classified based on their structure and function in the body. These are:
- Epithelial tissue: Covers body surfaces and lines organs
- Connective tissue: Supports, binds, and protects organs
- Muscular tissue: Enables movement through contraction
- Nervous tissue: Conducts impulses for coordination and control
2. What is epithelial tissue and its function?
Epithelial tissue forms the protective covering of all body surfaces and lines internal organs. Key functions include:
- Protection against pathogens and mechanical injury
- Absorption of nutrients (e.g., in the intestine)
- Secretion of enzymes, hormones, and mucus
- Sensory reception
3. What are the main types of connective tissue in animals?
Connective tissue in animals includes a variety of tissue types that connect, support, and anchor body parts. The main types are:
- Loose connective tissue (e.g., areolar tissue)
- Dense connective tissue (e.g., tendons, ligaments)
- Adipose tissue (fat storage)
- Skeletal tissue (bone and cartilage)
- Fluid connective tissue (blood and lymph)
4. What is muscle tissue? Name its types.
Muscle tissue is responsible for producing movement in animals through contraction and relaxation. There are three main types:
- Skeletal muscle – Voluntary muscles attached to bones
- Smooth muscle – Involuntary muscles found in internal organs
- Cardiac muscle – Involuntary muscle found only in the heart
5. What is the structure and function of nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue is specialised for transmitting electrical signals and coordinating body activities. Key features include:
- Comprised of neurons (nerve cells) and supporting glial cells
- Receives, processes, and transmits nerve impulses
- Forms the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
- Responsible for sensing stimuli and controlling responses
6. What are the functions of connective tissue?
Connective tissue performs several crucial functions in animals:
- Provides support and structure (e.g., bone, cartilage)
- Binds organs and tissues together
- Stores fat for energy (adipose)
- Transports nutrients and waste (blood)
- Defends against infections (lymphatic)
7. What is the difference between epithelial and connective tissue?
The main difference is that epithelial tissue covers and protects body surfaces, while connective tissue supports and connects different body parts.
- Epithelial tissue: Tightly packed cells, forms linings and coverings, avascular
- Connective tissue: Fewer, widely spaced cells, abundant extracellular matrix, vascular (except cartilage)
8. Why is blood considered a connective tissue?
Blood is considered a connective tissue because it connects different body systems by transporting nutrients, oxygen, hormones, and wastes.
- Composed of cells suspended in a fluid matrix (plasma)
- Originates from mesoderm (embryologically connective)
- Acts as a medium for communication between organs
9. What are the characteristics of nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue has unique characteristics that enable it to transmit impulses quickly:
- Contains specialized cells called neurons
- Possesses the ability to receive stimuli and transmit signals
- Supported by glial cells for nourishment and protection
- Highly responsive and coordinated for rapid communication
10. State the functions of muscle tissue.
Muscle tissue enables movement and mechanical work in animal bodies through contraction. Its functions include:
- Producing voluntary movements (skeletal muscles)
- Regulating internal movements (smooth muscles)
- Pumping blood (cardiac muscle)
- Maintaining posture and body position










