




Step-by-Step Practical Guide to Preparing Microscope Slides for CBSE Exams
Biology Experiment- Prepare Slide of Onion Peel and Cheek Cells
Introduction
Plants and Animals are eukaryotic organisms and contain very specific characters. They are advanced forms of organisms and are found in large populations. A eukaryotic cell contains many membrane bound organelles and a prominent nucleus with a nuclear membrane.
Table of Contents
The following article contains: -
Aim
Requirements
Theory
Methodology
Observations
Conclusion
Summary
Questions
Aim
To study onion peel under microscope and draw accurate labeled diagrams.
Requirements
Onion, Safranin, Glycerin, Compound microscope. Slides, Coverslips, forceps,etc.
Theory
Onion is a multicellular, eukaryotic organism which belongs to Kingdom Plante. An onion peel cell contains a cell wall, cell membrane, large vacuole at the center and prominent nucleus at the periphery of the cytoplasm. Safranin is stain used for staining plant cells as it colors all the organelles with a very prominent red color hence, helping in easy detection of various organelles under a microscope.
Procedure
For the onion peel experiment, cut an onion into two halves and remove a transparent membranous structure which is known as epidermal peel.
Take the peel with the help of a forceps in a watch glass containing water.
Add a few drops of safranin and let it stand for staining.
Wash the peel with water to remove extra stain
Transfer the peel on a glass slide with a brush.
Add a drop of glycerin over the peel and place the coverslip gently.
Remove extra stain/ glycerin with a blotting paper.
Observe the onion peel under microscope.
Observations
Red colored cells with prominent color on the periphery were observed.
Rectangular cells with thin cytoplasm are present enclosed within the cell wall.
Vacuole is large and centrally placed.
Nucleus is round in shape, deeply stained and present in each cell close to the periphery.
Result
The onion peel cell contains a large vacuole, prominent nucleus, thin cytoplasm and rectangular cells with a cell wall. Therefore, we can conclude that the above onion peel cell is a type of plant cell.
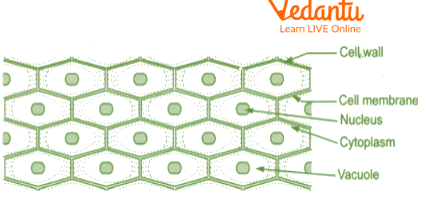
Onion peel cell diagram
To study Cheek cells under a microscope.
Requirements
Methylene blue, Glycerin, Compound microscope. Slides,forceps, toothpicks etc.
Theory
Humans are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms which belong to Kingdom Animalia. These cells contain a semi-permeable cell membrane, dense cytoplasm and the nucleus in the cheek cell is placed in the center. Cheek cells are squamous epithelium cells which are thin and flat and form a delicate lining inside the mouth.
Procedure
Gargle mouth with clean water.
Take a toothpick and scrap the epithelial cells from the inner lining of the cheek.
Place these scrapings over a clean slide and add a drop of water to it.
Evenly spread the cheek cells over the slide.
Add a drop of methylene blue and allow it to stain for 2-3 mins.
Remove the extra stain with blotting paper.
Add glycerin and place a coverslip gently and remove the excess with blotting paper.
Observe the onion peel under a microscope.
Observations
Large cells were seen which were irregular in shape.
The boundaries of cells are attached with each other.
Nucleus in cheek cells are deep blue-stained, round and present at the center of the cell.
The cytoplasm is dense and jelly-like, surrounded by a thin-walled cell membrane.
Result
The above cells do not contain a cell wall. The cell contains a dense cytoplasm. Nucleus in cheek cells are centrally placed. Therefore, we can conclude that the above specimen cell is a type of animal cell.
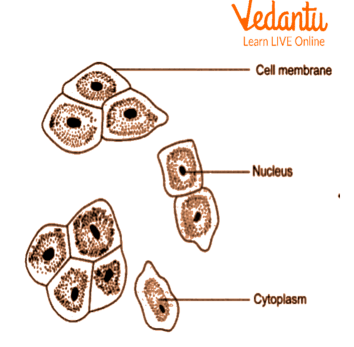
Internal structure of cheek cells
Precautions
Do not over stain the specimen
Place coverslip gently and avoid air bubbles
Remove excess stain and glycerine
Lab Manual Questions
1. In a plant cell diagram which organelles are present?
Ans: In a plant cell diagram, a cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus and vacuoles are present. It also contains mitochondria, golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum and chloroplast.
2. Cheek cells contain which organelle commonly?
Ans: Lysosomes are found commonly organelle in the cheek cells of the mouth.
3. How is the size of the nucleus related to the size of the cell?
Ans: Cell is a bigger entity and contains various organelles such as mitochondria, vacuoles etc. Nucleus is also an organelle and is present inside the cell. Hence, as compared to the size of the cell the nucleus is very small.
4. What is the main function of cheek cells?
Ans: Cheek cells secrete mucin which is an important part of mucous which in combination with the salivary glands keep the oral cavity moist and helps in the process of digestion.
Viva Questions
1. What is the basic structural and functional unit of life?
Ans: Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life.
2. Cell wall of plants is made up of which component?
Ans: Cell wall of plants is made up of cellulose which protects the inner parts of the cell.
3. Give two uses of cell membrane.
Ans: Cell membrane is a boundary which separates cytoplasm and all organelles from the outside environment. It is selectively permeable and hence facilitates the movement of materials across the cell.
4. Mention four organelles which are present in animal and plant cells.
Ans: Nucleus, Mitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi complex are found in both animal and plant cells.
5. Which are self-replicating organelles?
Ans: Mitochondria and Chloroplast both are self-replicating as they contain their own DNA.
6. Which organelle is only seen in animal cells?
Ans: Centrosome and it facilitates spindle fiber formation in cell division.
7. Which organelle is seen only in plant cells?
Ans: Chloroplast and it performs the function of photosynthesis.
8. Mounting of cells is always done in glycerin, why so?
Ans: Glycerin is a highly dense liquid and contains ample amount of moisture and hence prevents drying out of the cells.
9. Why should air bubbles be prevented?
Ans: When air bubbles are formed they cover parts of the cell which is under observation. Therefore, they should be avoided.
10. What is the significance of teasing?
Ans: Teasing separates all cells from each other so that they can be seen clearly under the microscope.
Practical Based Questions
1. Human cheek cells are commonly stained with
Methylene blue
Safranin
Crystal violet
Glycerin
Ans: Methylene blue
2. Nucleus in the cheek cell is________.
Placed centrally
Placed peripherally
Placed in the cell membrane
Placed inside the vacuoles
Ans: Placed centrally
3. Cheek epithelial cells are a type of_______.
Epithelial cells
Squamous epithelial cells
Cuboidal epithelial cells
None of these
Ans: Squamous epithelial cells
4. Which stain is used for staining onion peel?
Acetocarmine
Methylene red
Crystal violet
Safranin
Ans: Safranin
5. Seetha makes a cell diagram containing rectangular cells and chloroplast, mitochondria and vacuole. This cell is a_______.
Onion peel cell diagram
Animal cell diagram
Eukaryotic cell diagram
Prokaryotic cell diagram
Ans: Onion peel cell diagram
6. What is observed under the high power of a microscope?
Large cells, more in number
Small cells, less in number
Large cells, less in number
Small cells, more in number
Ans: Large cells, less in number
7. Which of the following is not seen in cells of squamous epithelium?
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Cell wall
Ans: Cell wall
8. Site of protein synthesis is ______.
Chloroplast
Ribosomes
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ans: Ribosomes
9. To observe an object at high power; the order of lens in a compound microscope is-
Objective 10X, eye piece 45X
Objective 45X, eyepiece 10X
Objective 10X, eyepiece 10X
Objective 45X, eyepiece 45X
Ans: Objective 45X, eyepiece 10X
10. Put in correct chronological order-
i) Remove cheek cells with toothpick
ii) Stain with methylene blue
iii) Clean the mouth with water
iv) Observe under microscope
i, ii, iii, iv.
iii, i, ii, iv
ii, iii, iv, i
iv, iii, ii, i
Ans: iii, i, ii, iv
Summary
Onion and Cheek cells experiments give us information regarding plant and animal cells. A plant cell contains, large vacuole and cell wall. Animal cells contain nucleus and cell membranes. Plant cells have a definite shape whereas animal cells are irregular in shape. Staining of cells helps in better visibility of cells and their organelles.
FAQs on CBSE Class 9 Biology: How to Prepare Onion Peel and Cheek Cell Slides (2025-26)
1. For the CBSE Class 9 practical exam (2025-26), what is the main objective of preparing temporary mounts of onion peel and human cheek cells?
The primary objective is to learn the correct procedure for preparing stained temporary mounts of plant (onion) and animal (cheek) cells. This experiment aims to help students observe the cells under a microscope, identify their key components like the nucleus, cell wall, and cell membrane, and ultimately differentiate between plant and animal cells based on their structural differences.
2. What are the most important observations to record from the onion peel slide experiment for exam marks?
For scoring well, you must record these key observations for onion peel cells:
- The cells are rectangular and compactly arranged in a brick-like pattern.
- Each cell is enclosed by a distinct and rigid cell wall, which is a characteristic feature of plant cells.
- A prominent, darkly stained nucleus is clearly visible, typically located at the periphery of the cell.
- A large, central vacuole dominates the cell, pushing the cytoplasm and nucleus to the side.
3. What are the key features to note in a human cheek cell slide to score full marks?
To get full marks for observing a human cheek cell slide, you should note the following:
- The cells are flat, thin, and irregular in shape with no definite arrangement.
- The outer boundary is the cell membrane; there is no cell wall.
- A prominent, darkly stained, and typically centrally located nucleus is visible.
- The cytoplasm appears as a lightly stained, granular substance filling the cell.
- The absence of a cell wall and a large central vacuole is a critical point of distinction.
4. Why is safranin preferred for staining onion peel cells while methylene blue is used for cheek cells? Is this an important step?
Yes, using the correct stain is a very important step. Safranin is used for onion cells because it imparts a pink or red colour that strongly stains the cell wall and nucleus, making plant cell structures clearly visible. Methylene blue is used for cheek cells as it is a basic stain that effectively colours the acidic components of the animal cell, such as the nucleic acids (DNA) in the nucleus, making it stand out with a deep blue colour.
5. Explain two key structural differences between onion peel cells and human cheek cells that are frequently asked in exams.
Two frequently asked and important differences are:
- Cell Wall: Onion cells possess a rigid cell wall made of cellulose located outside the cell membrane, which provides a fixed shape. Human cheek cells lack a cell wall entirely.
- Shape and Vacuole: Onion cells have a fixed, somewhat rectangular shape due to the cell wall and contain a large central vacuole. Cheek cells have an irregular shape and lack a large, permanent vacuole.
6. What are three essential precautions to take while preparing a temporary mount to avoid air bubbles and ensure a clear slide?
To ensure a clear, bubble-free slide, which is crucial for good marks, you must:
- Use a soft brush to transfer the delicate peel to avoid folding or tearing.
- Place the coverslip at a 45-degree angle to the slide and lower it gently using a needle. This allows air to escape and prevents bubble formation.
- Avoid using excess water or glycerine, as it can cause the coverslip to float and trap air underneath.
7. Why is a drop of glycerine added to the slide before placing the coverslip? What is its importance in this experiment?
Adding a drop of glycerine is an important step for two main reasons:
- It acts as a mounting medium that prevents the specimen from drying out quickly, giving you more time for observation under the microscope.
- It provides a clearer view of the specimen because its refractive index is close to that of the glass slide and coverslip, which reduces light distortion.
8. From an exam perspective, what is the final conclusion drawn by comparing the structures of onion and cheek cells?
The final and most important conclusion is that the onion cell, with its rigid cell wall and large vacuole, represents a typical plant cell. In contrast, the cheek cell, which lacks a cell wall and a large vacuole and has an irregular shape, represents a typical animal cell. This experiment visually demonstrates the fundamental structural differences between plant and animal cells as per the CBSE curriculum.




































