




Debt Free Countries: Top Nations without National Debt
Many countries around the world are struggling with their increased obligations in the form of debt but have maintained it quite low. A low level of debt shows less reliance on foreign borrowings. The best example can be taken from Hong Kong (it is a one of the debt free countries), whose economy has the least debt to GDP ratio. It is an almost debt free country. It has a well-regulated financial system and large foreign reserves. Its per capita GDP is the highest in the world, around £32,000. Countries with the most debt are Japan, Venezuela, Italy etc. Want to know which countries are debt-free? Here is a list of debt free countries.
Debt
What is Public Debt?
Public debt is defined as the total amount of liabilities which is followed by the government to meet the development budgets of the country. Public debt is generally expressed as the ratio of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The debt can be raised both in the form of external or internal means. Internal debt includes the debt borrowed within the country, and external debt is the debt that is put to lenders outside the country. Public debt is considered an important source for the government to meet its obligation and fulfil the needs of the economy.

Debt Needs to be Secured
Countries That Have the Biggest Amount of National Debt
According to the IMF (International Monetary Fund), the total amount of debt that is held by the government throughout the world has reached around $164 trillion in 2016. The debt by a country is measured in terms of the debt-to-GDP ratio. The highest debt countries have more obligations than those debt free countries. The countries with the highest debt countries are Venezuela, Japan, Greece, Italy, the USA, France, and the UK.
Debt to GDP Ratio
Debt-to-GDP ratio is measured as a country’s public debt to its GDP (Gross Domestic Product). This ratio indicates the country’s ability to repay its debts. When the debt to GDP ratio is low, it indicates that any economy produces more goods and services and is sufficient to pay back its debt. Higher debt-to-GDP ratio means they would be the highest debt countries and less debt-to-GDP ratio means they will be debt-free countries.
Top 10 Debt Free Countries 2025
The Highest Debt Countries are as Follows:
Below is the debt list of countries. The highest debt countries are Venezuela, Japan, Sudan, Greece, etc.
High Debt to GDP Ratio is a Danger Sign
Increasing public debt is a sign of worry. The research by the World Bank has shown that countries with debt-to-GDP ratios higher than 77% have faced economic slowdown over time. Debt-to-GDP ratio is an indicator of a country defaulting on its debt which may further lead to a financial crisis. The issue of debt has been increasing since the time of COVID-19. In this, the country with no debt is decreasing. With the increasing interest rate, government expenditure will slow down and will cause worry about the sustainability of the debt of the nation. The heavily indebted countries will feel the effect of these financial conditions, which will harm the growth prospects over time. Countries with no debt do not have such danger signs.
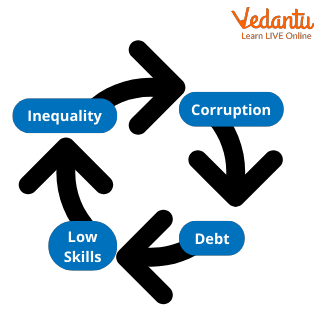
Problem with the Less Developed Countries
Countries with the Lowest National Debt
A low debt-to-GDP ratio is considered to be desired, but it does not indicate a healthy economy. These are called debt-free countries. Many developing and stagnant economies have a low debt-to-GDP ratio because both their debt and their GDP are quite low. If a country borrows from another country and invests for economic growth, then, in the long run, the economy could be a healthy economy because of continued learning and increased profit in future. As economic growth is not guaranteed, such a type of following could also be a bank fire, as in the case of Venezuela.
Countries with no debt or the least amount of debt are as follows:
Conclusion
With the increasing amount of debt around the globe, cost increases the risk of default and slow economic growth for the countries. Though with the help of debt, some countries are trying to overcome the slowdown caused by the pandemic lockdowns. Higher debt comes with slow growth potential and increases deficit spending with unpredictable long-term consequences. Countries with no debt have less risk, but they may further suffer in case of development.
FAQs on List of Debt Free Countries
1. Is there a country that has no debt?
There is no independent country that is completely debt-free. Almost every nation has some form of public debt, typically resulting from borrowing to fund projects or cover budget gaps. Having national debt is considered normal in modern economic systems.
2. What country is #1 in debt?
The country with the highest national debt is Japan. Japan's government debt exceeds 200% of its GDP, making it the top country in terms of the debt-to-GDP ratio. The Japanese government borrows mainly to support its social and economic programs.
3. Is the USA a debt-free country?
The United States is not a debt-free country. In fact, it has one of the largest public debts in absolute terms. The US government borrows money by issuing treasury securities to finance its budget deficits and fund various federal programs.
4. Is Norway in debt?
Yes, Norway does have public debt, but it keeps debt levels low compared to other developed nations. Norway manages its finances carefully, saving oil revenues in a national fund to help keep its public debt-to-GDP ratio modest.
5. Which countries have the lowest national debt?
Some countries with the lowest national debt as a percentage of GDP include:
- Brunei
- Hong Kong
- Estonia
- Botswana
6. Why do most countries have national debt?
Most countries have debt because governments borrow to pay for public services, build infrastructure, or handle shortfalls in revenue. Debt also lets them respond to emergencies or invest in the economy when needed, instead of raising taxes sharply or making sudden cuts.
7. What is meant by a debt-free country?
A debt-free country would have no government borrowing or outstanding loans. While this is rare, it means the country fully funds its budget with revenue, not by borrowing. In practice, most nations maintain some level of national debt for flexibility and stability.
8. How is a country's national debt measured?
A country’s national debt is typically measured as a percentage of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The formula is: $$ \text{Debt-to-GDP Ratio} = \frac{\text{Total Public Debt}}{\text{GDP}} \times 100 $$ This shows how large the debt is relative to the country’s economy.
9. Do debt-free countries have stronger economies?
Having no national debt does not automatically mean a stronger economy. Some advanced economies carry sustainable debt to invest in growth and services. Strong economies include good financial management, diverse income sources, and economic stability, not just low government borrowing.
10. Are there risks to having no national debt?
A debt-free country may face challenges such as limited flexibility during crises. Borrowing gives governments a tool to manage emergencies and invest in growth. Without any debt, responding to unforeseen needs might mean cutting services or raising taxes abruptly.
11. How do countries reduce their national debt?
Countries reduce national debt by:
- Increasing revenue through taxes
- Reducing public spending
- Privatizing state assets
- Growing the economy
12. Can a country erase all its national debt?
Completely erasing national debt is possible but rare. It would require surplus budgets for many years, careful financial planning, and political will. Most countries choose to keep manageable, sustainable levels of debt to maintain economic flexibility and support development.





















