
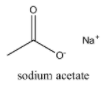
Sodium acetate on heating with soda lime produce:
(A) $C{{H}_{4}}$
(B) ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$
(C) ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}$
(D) ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$
Answer
527.8k+ views
Hint: Sodium salt of carboxylic acid on heating with soda lime produces alkane with one less carbon atom than carboxylic acid. Soda-lime is a mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide. Acetic acid has two carbon atoms. It is a decarboxylation reaction as there is the elimination of carbon dioxide from a carboxylic acid.
Complete step by step solution:
-Decarboxylation is a method to prepare alkane using sodium salt of carboxylic acid.
-This method can be used when one less carbon atom than carboxylic acid is required or when the number of carbon atoms is to be reduced by one.
-When sodium salt of the carboxylic acid is treated with soda lime which is a mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide, carbon dioxide is eliminated so an alkane is produced with one less carbon atom than carboxylic acid and sodium bicarbonate is produced as a by-product.
-Calcium oxide is used so Sodium hydroxide can be easily handled. Sodium hydroxide is highly hygroscopic and easily forms concentrated sodium hydroxide when exposed to air. Soda-lime does not absorb moisture easily.
-Soda-lime has the ability to absorb carbon dioxide. When carbon dioxide is eliminated from carboxylic acid, it reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium carbonate.
\[C{{H}_{3}}COONa+NaOH\xrightarrow{CaO,\Delta }C{{H}_{4}}+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\]
When sodium acetate on heating with soda lime, methane is produced.
Sodium acetate on heating with soda lime produce: $C{{H}_{4}}$, which is option (A)
Note: In decarboxylation, the sodium salt of carboxylic acid on heating with soda lime produces alkane with one less carbon atom than a carboxylic acid. In decarboxylation, the product is alkane having one less carbon atom than a carboxylic acid. If ethane is to be prepared, then sodium propionate should be used. IF carboxylic acid has n number of carbon atoms, then alkane produced will have (n-1) carbon atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
-Decarboxylation is a method to prepare alkane using sodium salt of carboxylic acid.
-This method can be used when one less carbon atom than carboxylic acid is required or when the number of carbon atoms is to be reduced by one.
-When sodium salt of the carboxylic acid is treated with soda lime which is a mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide, carbon dioxide is eliminated so an alkane is produced with one less carbon atom than carboxylic acid and sodium bicarbonate is produced as a by-product.
-Calcium oxide is used so Sodium hydroxide can be easily handled. Sodium hydroxide is highly hygroscopic and easily forms concentrated sodium hydroxide when exposed to air. Soda-lime does not absorb moisture easily.
-Soda-lime has the ability to absorb carbon dioxide. When carbon dioxide is eliminated from carboxylic acid, it reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium carbonate.

\[C{{H}_{3}}COONa+NaOH\xrightarrow{CaO,\Delta }C{{H}_{4}}+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\]
When sodium acetate on heating with soda lime, methane is produced.
Sodium acetate on heating with soda lime produce: $C{{H}_{4}}$, which is option (A)
Note: In decarboxylation, the sodium salt of carboxylic acid on heating with soda lime produces alkane with one less carbon atom than a carboxylic acid. In decarboxylation, the product is alkane having one less carbon atom than a carboxylic acid. If ethane is to be prepared, then sodium propionate should be used. IF carboxylic acid has n number of carbon atoms, then alkane produced will have (n-1) carbon atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




