
The correct order of basicity of amines in water is
A. (CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N>CH_{3}NH_{2}
B. CH_{3}NH_{2}>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N
C. (CH_{3})_{3}N>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>CH_{3}NH_{2}
D. (CH_{3})_{3}N>CH_{3}NH_{2}>(CH_{3})_{2}NH
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Amines are important organic compounds formed by the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom present in amine possesses a lone pair of electrons due to which amines are basic.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
According to the lewis concept, a base is a chemical species that can donate a pair of electrons to another chemical species.
So, amines are basic.
The basicity of amines is associated with their structure.
Amines donate a pair of electrons and form an ammonium cation.
The more stable this cation, the more will be its basicity.
The basicity of amines in an aqueous solution is governed by three effects:-
I) +I-effect of the alkyl group
II) H-bonding with water molecules
III) Steric effects
+I-effect of the alkyl group
We know that the alkyl groups are the electron releasing group or +I group.
With the increase in the number of alkyl groups, the +I effect increases.
Due to this, the positive charge present on the cation gets dispersed. This increases the stability of the action.
So, the basicity of amines should be in the order
(CH_{3})_{3}N>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>CH_{3}NH_{2}.
H-bonding with water molecules
Ammonium cation in an aqueous solution
forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This gives the cation more stability.
The formation of H-bonding with water molecules depends on the number of H-bonds.
More hydrogen atoms on nitrogen atoms greater will be H-bonding with the water molecules which will, in turn, increase the stability of an ammonium action in an aqueous solution.
Primary amines will have more H-bonding as it has three hydrogen atoms followed by secondary and tertiary amines.
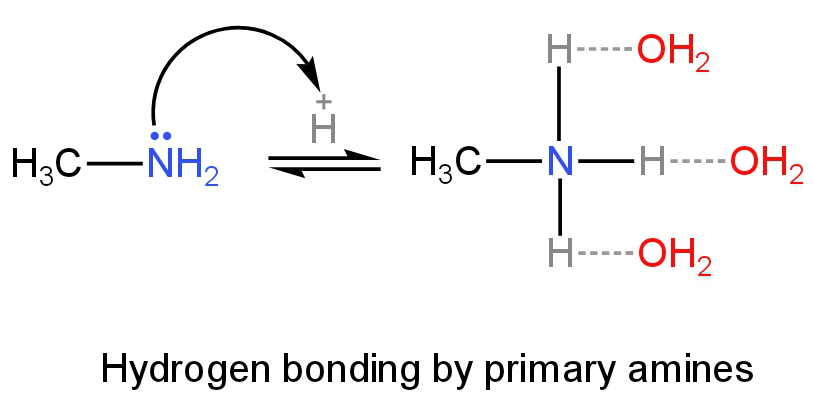
Image: H-bonding of primary amines in an aqueous solution.
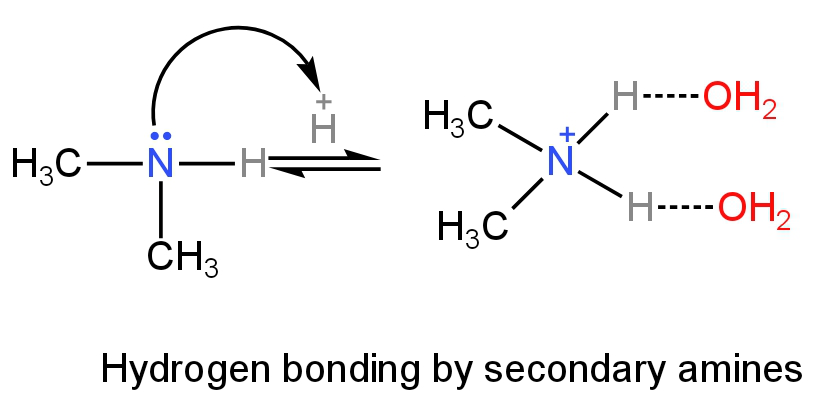
Image: H-bonding of secondary amines in an aqueous solution.
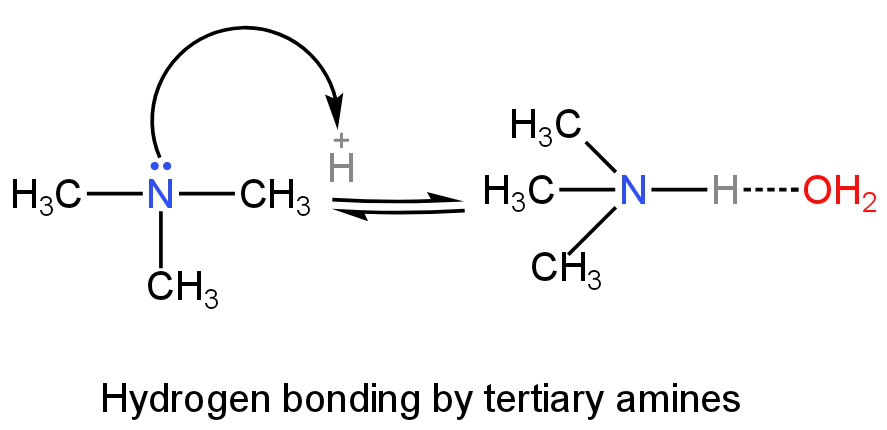
Image: H-bonding of tertiary amines in an aqueous solution.
So, the basicity order will be in the order,
CH_{3}NH_{2}>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N.
Steric effects
In the case of ammonium cation derived from tertiary amines due to the presence of three bulky methyl groups, there is some steric repulsion to H-bonding. This decreases the basicity of tertiary amines.
So, the basicity order will be in the order,
CH_{3}NH_{2}>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N.
The three effects i.e., the +I effect, H-bonding and steric factors favour the secondary amines. So, secondary amines are the strongest bases.
Primary amines have one alkyl group which does not give rise to steric repulsion to H-bonding.
So, primary amines are stronger than tertiary amines.
The basicity of tertiary amines is reduced due to steric repulsion to H-bonding.
The correct order of basicity of amines in an aqueous solution is
(CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N>CH_{3}NH_{2}.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Ammonium cation forms hydrogen bonding with water molecules. This is due to the solvation effect. The solvation effect is defined as the interaction of dissolved solute molecules with solvent molecules. In the given question, ammonium cation is the solute and water is the solvent. The solvation of a solute by water is known as hydration.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
According to the lewis concept, a base is a chemical species that can donate a pair of electrons to another chemical species.
So, amines are basic.
The basicity of amines is associated with their structure.
Amines donate a pair of electrons and form an ammonium cation.
The more stable this cation, the more will be its basicity.
The basicity of amines in an aqueous solution is governed by three effects:-
I) +I-effect of the alkyl group
II) H-bonding with water molecules
III) Steric effects
+I-effect of the alkyl group
We know that the alkyl groups are the electron releasing group or +I group.
With the increase in the number of alkyl groups, the +I effect increases.
Due to this, the positive charge present on the cation gets dispersed. This increases the stability of the action.
So, the basicity of amines should be in the order
(CH_{3})_{3}N>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>CH_{3}NH_{2}.
H-bonding with water molecules
Ammonium cation in an aqueous solution
forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This gives the cation more stability.
The formation of H-bonding with water molecules depends on the number of H-bonds.
More hydrogen atoms on nitrogen atoms greater will be H-bonding with the water molecules which will, in turn, increase the stability of an ammonium action in an aqueous solution.
Primary amines will have more H-bonding as it has three hydrogen atoms followed by secondary and tertiary amines.

Image: H-bonding of primary amines in an aqueous solution.

Image: H-bonding of secondary amines in an aqueous solution.

Image: H-bonding of tertiary amines in an aqueous solution.
So, the basicity order will be in the order,
CH_{3}NH_{2}>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N.
Steric effects
In the case of ammonium cation derived from tertiary amines due to the presence of three bulky methyl groups, there is some steric repulsion to H-bonding. This decreases the basicity of tertiary amines.
So, the basicity order will be in the order,
CH_{3}NH_{2}>(CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N.
The three effects i.e., the +I effect, H-bonding and steric factors favour the secondary amines. So, secondary amines are the strongest bases.
Primary amines have one alkyl group which does not give rise to steric repulsion to H-bonding.
So, primary amines are stronger than tertiary amines.
The basicity of tertiary amines is reduced due to steric repulsion to H-bonding.
The correct order of basicity of amines in an aqueous solution is
(CH_{3})_{2}NH>(CH_{3})_{3}N>CH_{3}NH_{2}.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Ammonium cation forms hydrogen bonding with water molecules. This is due to the solvation effect. The solvation effect is defined as the interaction of dissolved solute molecules with solvent molecules. In the given question, ammonium cation is the solute and water is the solvent. The solvation of a solute by water is known as hydration.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




