




How to Identify Before, After, and Between Numbers Easily
You must know the counting numbers and operations related to counting. How many minutes will it take to count from 1 to 100? Let’s try and record your time. If you are a master in counting then you will easily learn the concept of before, after, and between numbers. This concept will be like a number game for you. You will just learn the numbers that come after, before, and between the provided numbers in this article. In maths before and after numbers concept is very important to grasp the concept of numbers.
Before After Between
How to Teach Before Numbers
Knowing the location of things is important in maths. To teach before, after, and between kids can do several exercises daily with them such as:
Try it with a Wall Clock: Take a wall clock, with the help of visual representation ask them what comes before 3 in the clock or what comes after 9 in the clock, and make them learn before, after, and between with the help of the wall clock.
Try it with Fruits: Bring their favourite fruits and line them up and ask your child which fruit is before, after, or between.
Try it with Toys: Bring their favourite toys and line them up as if they are going somewhere and ask them what comes before, after, and between.
Remember practice makes a man perfect, so keep trying such activities with them daily.
What comes After Before Between
Numbers that come before are always smaller than the given number. In case of between count forward or backward to find the number that comes between. It all depends on what number is chosen. The number that comes after is always greater than the given number.
Maths Before, After, and Between Numbers
We have a maths counting game is for kids to learn the number that comes between, a number that comes before, and the number that comes after. Counting before, after, and between numbers up to 10 improves the child’s counting skills. Number counting is a basic maths skill that will help children to recognize the order of the numbers.
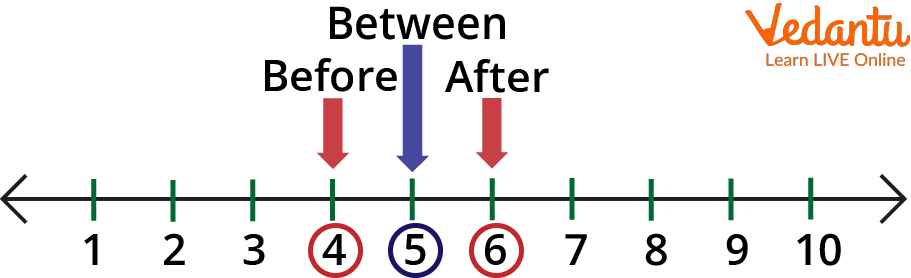
Counting Numbers Before, After, and Between
On The Number Line:
Number 4 is before number 5,
Number 6 is after number 5,
Number 5 is between numbers 4 and 6.
Before, After, and Between Number Activities for Kindergarten
1. Gather up some of your children’s favorite toys. You will need three Stuffed animals, toy people, cars, etc

Toys
2. Line the toys up as if they are going somewhere. For animals, set a bowl in front of the first one and tell your child they are all going to the bowl to get a drink. This helps your children understand their positional relationship, by understanding that the first one in line will come before the others to get a drink.
Some other ideas for lining up the toys in this step include: Placing them in front of a gate, putting cars in front of a garage, and putting people in front of a booth. Ensure your child knows they are lined up to go somewhere.
3. On index cards write the words BEFORE, BETWEEN, and AFTER. Label each toy with its position in line.
4. Tell your children the position of the toys using the words “before, between, and after”.
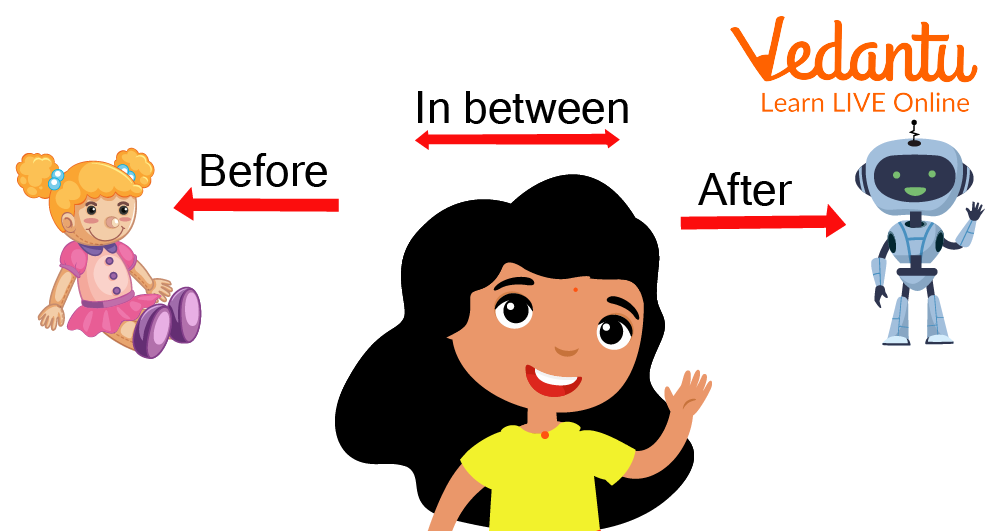
Girl and Toys
Talk to them about who will arrive at the bowl first and explain that means he comes "before" the other toys.
Next, explain who will arrive at the bowl last and explain that this means the toy comes "after" the others.
Explain to the children that the one in the middle is "in between."
In this way, with the help of toys, kids can easily learn the concept of what comes after, before, and between. When they gave correct answers they replace the toys with numbers.
Solved Examples
Q1. What comes before and after the following numbers?
54, 12, 47, 34
Ans: Before the numbers = 53, 11, 46, 33
After the numbers = 55, 13, 48, 35
Q2. What comes between the numbers?
34__36
67__69
80__82
12__14
Ans: (a) 35, (b) 68, (c) 81, (d) 13
Practice Questions
Q1. Identify what number comes before.
(a) ------ ← 15 (b) ------ ← 6
(c) ------ ← 28 (d) ------ ← 44
Ans: (a) 14, (b) 5, (c) 27, (d) 43
Q2. Identify what number comes after.
(a) 31 → ------ (b) 46 → ------
(c) 28 → ------ (d) 5 → ------
Ans: (a) 32, (b) 47, (c) 29, (d) 6
Q3. Identify what number comes between.
(a) 28 ------ 30 (b) 25 ------ 27
(c) 18 ------ 20 (d) 12 ------ 14
Ans: (a) 29, (b) 26, (c) 19, (d) 13
Summary
Having an understanding of position in space and how things are positioned relative to each other is part of a child’s visual perception and cognitive development. You can play various games and do fun activities which will help them grasp the concepts and give them some early mathematics such as before, after, and between. In this article, the importance of this concept is discussed with the help of some daily life activities and fun games for kids. Like they can use this concept with a clock at home. In this way, this game of numbers is discussed here in a joyful way.
FAQs on Before, After, and Between Numbers Explained
1. What is before, after, and between numbers?
In mathematics, the before number is the number that comes just before a given number when counting, the after number comes immediately after, and the between number is exactly in the middle of two other numbers. For example, considering the number 5:
- The number before 5 is 4.
- The number after 5 is 6.
- The number between 4 and 6 is 5.
2. What is the name of 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9?
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 are called digits or numerals. Collectively, they are known as Arabic numerals or the decimal number system. All other numbers can be formed by combining these digits in various ways. On Vedantu, students learn to use these basic digits as a foundation for arithmetic and number sense.
3. What number is inbetween 1 and 2?
The number between 1 and 2 can vary depending on the context:
- If considering whole numbers, there is no integer between 1 and 2.
- For decimal numbers or fractions, there are infinitely many possibilities such as $1.5$, $\frac{3}{2}$, or $1.25$.
4. What is meant by between numbers?
The phrase between numbers refers to any value that lies in the interval separating two numbers. For example, between 2 and 3, numbers like 2.1, 2.5, or $\frac{7}{3}$ are considered between numbers. This understanding supports mathematical concepts like ranges, intervals, and can be visualized effectively through Vedantu’s interactive math tools and resources.
5. How do you teach before, after, and between numbers to young learners?
Teaching before, after, and between numbers to young learners is most effective using engaging techniques such as:
- Number lines: Visual aids help students see the order and spacing of numbers.
- Interactive games: Activities where children place cards in sequence or fill in missing numbers.
- Story problems: Real-life situations that relate to ordering numbers.
6. Why is understanding before, after, and between numbers important in early math?
Understanding the concepts of before, after, and between numbers is crucial for:
- Building number sense and counting skills
- Laying the foundation for addition, subtraction, and sequencing
- Boosting logical thinking and pattern recognition
7. Can the concept of between numbers be applied to negative numbers as well?
Yes, the idea of between numbers applies to negative numbers too. For example, the number between $-3$ and $-2$ could be $-2.5$ or $-2.1$. Just like with positive numbers, there are infinitely many numbers between any two distinct negative numbers, and Vedantu’s courses explain these concepts clearly for all number types.
8. How do number lines help in understanding before, after, and between numbers?
Number lines are a practical way to visualize before, after, and between numbers. Each point on a number line represents a number, allowing students to see which numbers come before, after, or fall between others. Number lines are extensively used in Vedantu’s lessons for interactive demonstrations and exercises, reinforcing these math concepts visually.
9. What activities can reinforce the concept of between numbers at home?
To reinforce between numbers at home, try:
- Counting games while walking up stairs or setting the table
- Number puzzles and worksheets with missing or in-between numbers
- Using household objects to make simple sequences
- Online practice sessions via Vedantu’s educational resources
10. How does learning before, after, and between numbers prepare students for advanced math?
Learning before, after, and between numbers provides essential skills for:
- Ordering and comparing numbers in sequences or lists
- Understanding mathematical operations such as addition and subtraction
- Moving on to number patterns, skip counting, and basic algebra























