




Rhizopus- Classification, Characteristics, and Significance for NEET Aspirants
Rhizopus, a cosmopolitan fungus, is found in moist places like soil, decaying vegetables, fruits, stale bread, etc. One of the most common species of these fungi is known as bread mould, Rhizopus stolonifer.
The body structure of these fungi is multinucleated, built up of coenocytic and branching mycelia. Most Rhizopus fungi act as decomposers, saprobic, which feed on dead organic substances. Some species of this fungus are pathogenic or parasitic, and can also cause fatal infection in both plants and humans, termed as mucormycosis.
Classification
These are filamentous fungi within the Rhizopodaceae family under the Zygomycota phylum. They can be classified by zygospores production during their sexual reproduction.
Example: Pin mould, Black bread mould, etc.
Here is The Rhizopus Classification Described in A Tabular Form:
Common Examples
Rhizopus Oryzae – This fungus helps to produce cortisone and lactic acid. These products are used to ferment alcoholic beverages like beer, wine, etc. and biosorption of heavy metals.
Rhizopus Microsporus – It is used while fermenting soybean products.
Rhizopus Stolonifer – This is the most commonly used fungus in producing chemicals like fumaric acid, cortisone, lactic acid, etc. Moreover, it also causes fruit diseases like rotting.
Rhizopus Delemar – It produces biotin and fumaric acid.
Rhizopus Diagram and Structure
These fungi grow fast and come with a cotton-like appearance.
The branching mycelia in Rhizopus body comprised of three kinds of hyphae – rhizoids, stolons, and sporangiophores.
Stolons are aerial and signify the internodal region. These form arches and connect the substratum. This substratum helps in forming nodes.
Rhizoids are developed at the nodal regions. These are branched and can hook the mycelium and substratum to absorb food.
Sporangiophores, the reproductive mycelia, are aerial as well as branched.
The cytoplasm of rhizopus call is multinucleated, and the cell wall is developed by chitin. Also, other cell organelles like endoplasmic reticulum, oil droplets, vacuoles, and mitochondria are present in the cytoplasm.
These fungi can reproduce by sexual, asexual, and vegetative methods.
Here is the Bread Mould Diagram for Reference
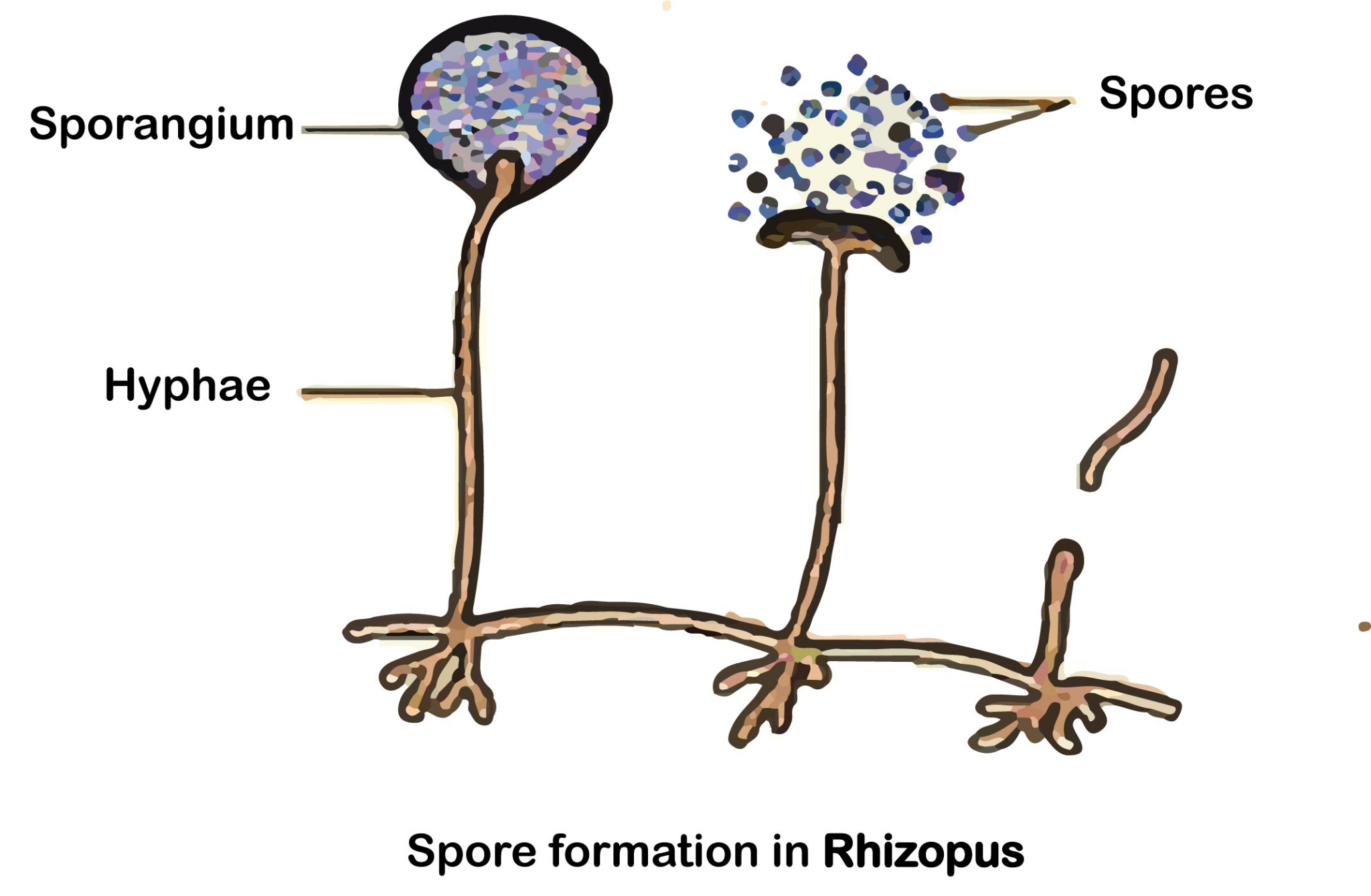
Life Cycle
Following is a detailed discussion on the life cycle of Rhizopus. They can reproduce by three methods-
Vegetative
The vegetative reproduction process occurs by fragmentation. The stolons divide into several fragments, and each part grows as a complete mycelium individually.
Asexual
Asexual reproduction happens by the spore formation in Rhizopus. These spores can be chlamydospores and sporangiospores.
Sporangiospores Formation
Sporangiospores are created in the sporangia of aerial mycelium. They are formed terminally.
From the upper portion of rhizoidal nodes, sporangiospores are formed.
The swelling of the apical part helps in the formation of the sporangium. During this time, the cytoplasm and nuclei move apically.
Sporangiospores grow inside the sporangium, and they are non-motile and multinucleated.
Later, the cytoplasm divides into two sections. One section develops into a more concentrated peripheral region along with a large number of nuclei. However, the other part creates a central columella region along with more vacuoles but a fewer number of nuclei.
After maturation, the sporangium wall breaks, and sporangiospores step out as powdery mass.
With the availability of favourable substratum and condition, each spore develops into separate mycelium by germination.
Chlamydospores Formation
The formation of chlamydospores occurs in unsuitable conditions. After septae formation and protoplasm accumulation, an intercalary part of mycelium creates. This part has a thick wall, and it detaches from the primary mycelium as it dries. Other parts become dormant and wait for suitable conditions to return for germinating to new mycelium.
Sexual
The sexual reproduction process happens by merging of two hyphae. Usually, these fungi species are heterothallic. This means they have different mycelium for + and – as mating strains. Example: R. stolonifer.
However, Some Homothallic Fungi Are Also Available, Like R. Sexualis.
During this reproduction method, both hyphae come closer. In their mycelia, an outgrowth, called progametangia, develops.
Cytoplasm and nuclei start moving towards the apical region. Both progametangia are contacted.
Through septae formation, the apical region detaches from the other part of hyphae. This part is called gametangia.
Gametangia fuse and develop a multinucleated structure.
After plasmogamy and karyogamy, a diploid zygote is developed. It is termed as a zygospore. Other unpaired nuclei eventually degenerate.
The zygospores start growing and create a thick wall. They become dormant in adverse conditions. In favourable conditions, zygospores initiate germination.
Zygospores’ inner walls turn into promycelium that form the germs sporangiophore as well as germ sporangium.
After meiosis, haploid meiospores are developed. By rupturing the germ sporangium wall, these meiospores come out and form new mycelia.
Time for Your Final Revision!
As you are preparing for NEET 2025, the above content can help you in revising the topic of Rhizopus quickly. Moreover, by learning the Rhizopus diagram, you can easily memorise its structure, while the bullet points can help you look through important points quickly.
However, besides practising and studying for NEET, you should also take care of your health. With increasing temperature, you must keep hydrating your body with a good amount of water. Also, you can do some physical activities like walking, jogging, practising yoga, etc. to be healthy and fit. In these last few days, you can track your progress too by appearing for mock tests while also practising last year’s question papers.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on NEET Rhizopus (The Bread Mould) - Biology Preparation
1. What is The Disease Caused By Rhizopus?
Rhizopus can cause a rare and fatal disease called mucormycosis. Usually, burn victims, malnourished and diabetic patients, individuals with AIDS, or some specific cancers can be affected by R. arrhizus fungus and consequently this disease.
2. What are The Primary Usages of Rhizopus?
These fungi are majorly used in various industrial processes which include alcohol fermentation, heavy metal biosorption, etc.
3. How Dangerous Can Black Mould Be?
Usually, black mould or bread mould present on the bread surface, is not dangerous if consumed by an individual. However, for some individuals, specific moulds can lead to severe allergic reactions, vomiting, nausea, and indigestion.
4. What Is Rhizopus?
Rhizopus is a genus of saprophytic fungi that belong to the Zygomycota division. They typically thrive on decaying organic matter, aiding in decomposition. Their coenocytic hyphae (lacking cross walls) are a key distinguishing feature.
5. How Does Rhizopus Reproduce?
Rhizopus reproduces both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction usually involves the formation of sporangiospores within sporangia, while sexual reproduction occurs through the fusion of compatible hyphae to produce zygospores.
6. What Are the Common Uses of Rhizopus in Industry?
example, Rhizopus oryzae is used in traditional food fermentation processes, such as making tempeh. It’s also involved in enzyme production and certain biochemical transformations.
7. Is Rhizopus Harmful to Humans?
While many species of Rhizopus are beneficial saprophytes, certain strains (especially Rhizopus oryzae) can cause opportunistic infections like mucormycosis, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. Early detection and medical intervention are vital.
8. How Can NEET Aspirants Study Rhizopus Effectively?
Focus on the morphology, reproduction (both sexual and asexual), and economic importance of Rhizopus. Labelled diagrams, comparison charts with other fungi, and practicing MCQs on fungal biology can strengthen your conceptual understanding for NEET.
9. What Makes Rhizopus Important for NEET Biology?
Rhizopus exemplifies fundamental fungal biology concepts that NEET frequently tests—like saprophytism, coenocytic hyphae, and zygomycetes. Understanding these key features helps students quickly tackle related exam questions.
10. Can Rhizopus Survive in Various Environmental Conditions?
Yes. Rhizopus is quite versatile and thrives in moist, nutrient-rich environments such as bread, fruits, and decaying organic matter. However, it can’t survive in conditions lacking essential moisture or organic substrates.
11. How Do Rhizopus Infections Spread?
Infections primarily spread via spores in the air. When these spores land on suitable surfaces (e.g., decomposing food) or are inhaled by immunocompromised individuals, they can germinate and potentially cause infection.























