
Define cubit, hand-span, arm-length, and foot-span.
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: Measurement is the process of comparing an unknown quantity to a known quantity.
A measuring system is made up of a set of units of measurement as well as the rules that connect them. We used to use body parts for informal measurement systems such as foot length, cubit, and hand-span, which were inexact and differed from person to person. Non-standard measurement units were used before the conventional units of length measurement were developed.
Complete answer:
We measure a variety of little objects in our daily lives using both standard and nonstandard length measuring units. The two sorts of units used to measure length are non-standard units and standard units.
Nonstandard measuring lengths include finger width, pace, hand span, foot span, arm span, and a cubit. These measurement units were used before the conventional units of length measurement were developed.
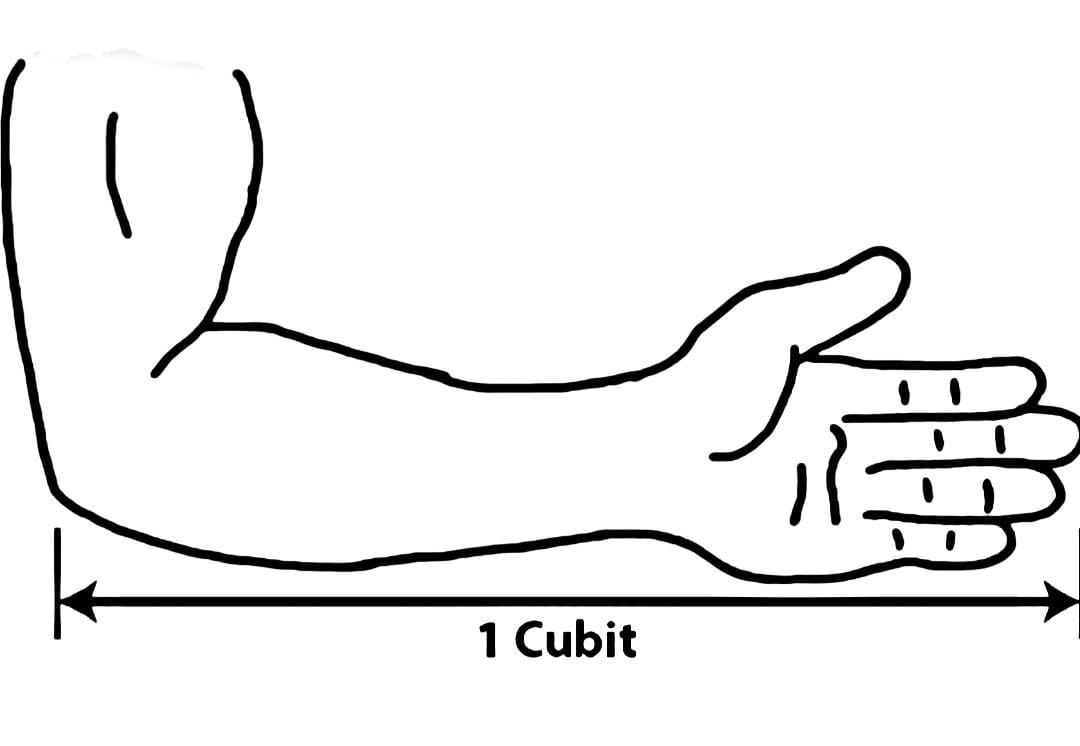
Cubit:-
When your arm is extended, the cubit is the distance between your elbow and the tip of your middle finger.
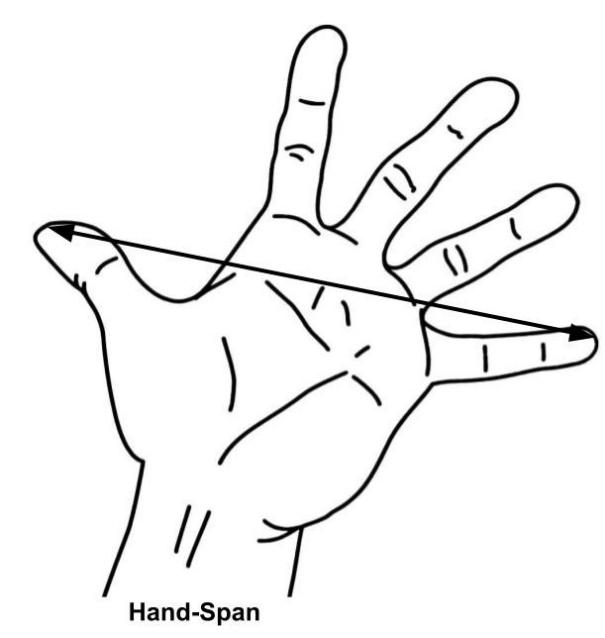
Hand-span: -
When your hand is spread out, the hand-span is the distance between the tips of your little finger and the tips of your thumb.
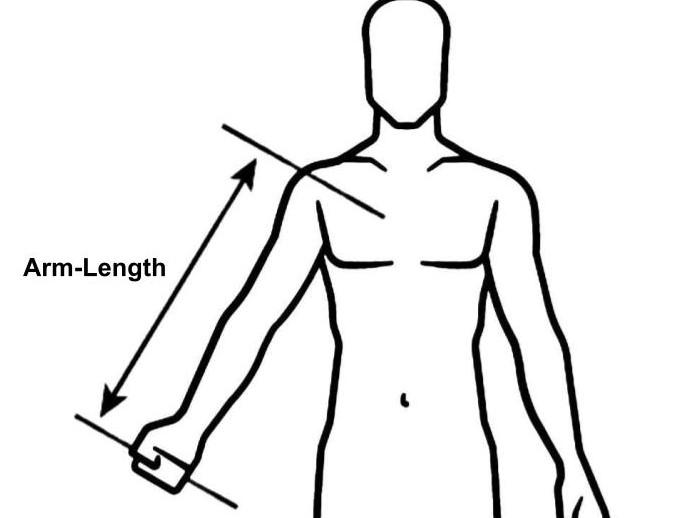
Arm-length: -
The distance between one end of an individual's arms (measured at the fingertips) and the other when elevated parallel to the ground at shoulder height at an angle is known as arm-length or reach (also referred to as wingspan, or written arm-span).
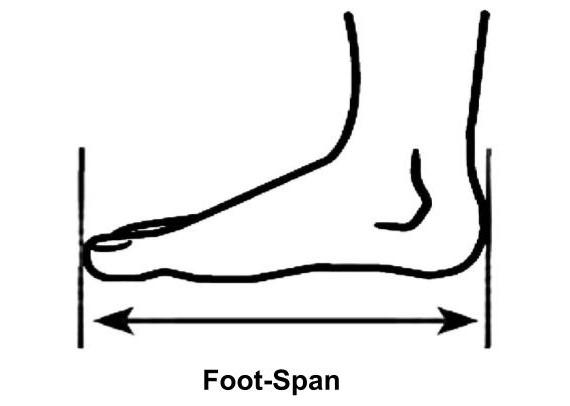
Foot Span:-
The foot span is the distance between the point of the toe and the heel of the foot.
Note:
It should be noted that the metrics had to be standardised. The Imperial and US customary units, as well as the International System of Units (the modern form of the metric system), were all harmonised globally.
A measuring system is made up of a set of units of measurement as well as the rules that connect them. We used to use body parts for informal measurement systems such as foot length, cubit, and hand-span, which were inexact and differed from person to person. Non-standard measurement units were used before the conventional units of length measurement were developed.
Complete answer:
We measure a variety of little objects in our daily lives using both standard and nonstandard length measuring units. The two sorts of units used to measure length are non-standard units and standard units.
Nonstandard measuring lengths include finger width, pace, hand span, foot span, arm span, and a cubit. These measurement units were used before the conventional units of length measurement were developed.
Cubit:-
When your arm is extended, the cubit is the distance between your elbow and the tip of your middle finger.

Hand-span: -
When your hand is spread out, the hand-span is the distance between the tips of your little finger and the tips of your thumb.

Arm-length: -
The distance between one end of an individual's arms (measured at the fingertips) and the other when elevated parallel to the ground at shoulder height at an angle is known as arm-length or reach (also referred to as wingspan, or written arm-span).

Foot Span:-
The foot span is the distance between the point of the toe and the heel of the foot.

Note:
It should be noted that the metrics had to be standardised. The Imperial and US customary units, as well as the International System of Units (the modern form of the metric system), were all harmonised globally.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




