




How Do You Calculate the Capacitance of a Spherical Capacitor?
Spherical capacitance is key for analyzing energy storage in spherical symmetry, essential for physics competitions like JEE and NEET.
A spherical capacitor features two concentric conductive spheres with radii $a$ (inner) and $b$ (outer), separated by an insulating medium.
Imagine an onion, with layers representing the spherical shells; charge stored between layers creates the spherical capacitance.
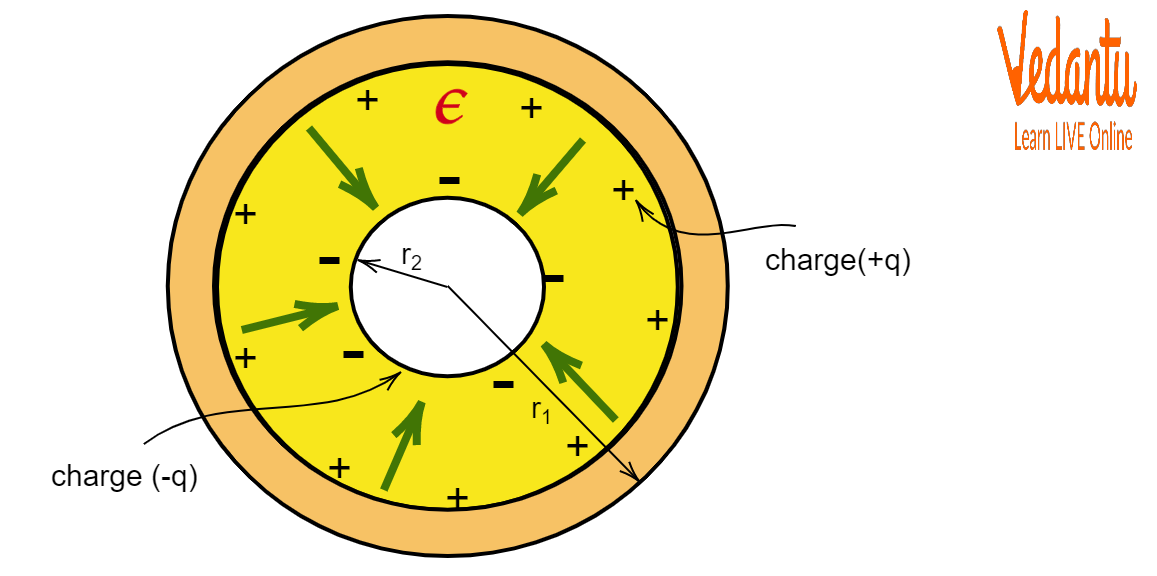
What Is Spherical Capacitance?
Capacitance quantifies an object’s ability to store charge per unit potential difference; for a spherical capacitor, spherical geometry governs this property.
According to Gauss’s Law, the field outside the spherical capacitor depends only on total charge, causing symmetry in calculations.
Derivation of the Capacitance Formula
Let a charge $+Q$ be given to the inner sphere and $-Q$ to the inner surface of the outer sphere, ensuring electric fields exist only in the region between the shells.
Applying Gauss’s Law for $a < r < b$: $E = \dfrac{Q}{4\pi \varepsilon_0 r^2}$, where $r$ is the distance from the center.
The potential difference between spheres is calculated by integrating the electric field from $a$ to $b$: $\Delta V = -\int_{a}^{b} E \; dr = \dfrac{Q}{4\pi \varepsilon_0} \left(\dfrac{1}{a} - \dfrac{1}{b}\right)$
By definition, $C = \dfrac{Q}{\Delta V}$, so substituting the above yields $C = 4\pi \varepsilon_0 \dfrac{ab}{b - a}$.
If the outer shell's radius tends to infinity ($b \to \infty$), the formula reduces to the capacitance of an isolated sphere: $C = 4\pi \varepsilon_0 a$.
Comparison With Other Capacitors
Spherical capacitors differ from parallel plate types as their field and potential are governed by radial symmetry, not planar geometry.
| Capacitor Type | Capacitance Formula |
|---|---|
| Parallel Plate (Vacuum) | $C = \varepsilon_0 \dfrac{A}{d}$ |
| Cylindrical | $C = 2\pi \varepsilon_0 \dfrac{l}{\ln(b/a)}$ |
| Spherical | $C = 4\pi \varepsilon_0 \dfrac{ab}{b-a}$ |
Physical Explanation and Visualization
Capacitance depends on both radii; increasing the separation (difference in radii) decreases the capacitance, while increasing surface area boosts storage ability.
The curved geometry ensures the electric field’s magnitude weakens with distance, leading to the derived potential and capacitance expressions.
Types of Spherical Capacitors and Real-World Use
- Concentric spherical shells with air/vacuum as dielectric
- Shells separated by a dielectric with permittivity $\varepsilon$
- Single isolated spherical conductors
To explore how materials between conductors affect results, review Permittivity in Coulomb's Law.
Solved Example
Suppose a spherical capacitor has $a = 5 \; \mathrm{cm}$, $b = 10 \; \mathrm{cm}$, and vacuum between. Calculate its capacitance.
First, convert to meters: $a = 0.05 \; \mathrm{m}$, $b = 0.10 \; \mathrm{m}$. $C = 4\pi \varepsilon_0 \dfrac{(0.05)(0.10)}{0.10-0.05}$
$\varepsilon_0 = 8.85 \times 10^{-12} \; \mathrm{F/m}$. Substitute values: $C = 4\pi \cdot 8.85 \times 10^{-12} \cdot \dfrac{0.005}{0.05}$
$C \approx 1.11 \times 10^{-12} \ \mathrm{F} = 1.11 \ \mathrm{pF}$
Key Points for JEE and NEET
- Spherical capacitors are tested for formula derivation and concept application
- Problem statements often involve varying radii or adding dielectrics
- Recall the isolated sphere formula is a limiting case
Concepts like charge induction, field lines, and symmetry are essential, as covered in Fundamentals of Electrostatics.
Common Mistakes and JEE Traps
- Mixing up inner/outer radii or forgetting unit conversions
- Overlooking the effect of dielectrics in denominators
- Treating it like a parallel plate formula
Always check limits and mathematical behavior as $b \to a$ or $b \to \infty$, especially when combining formulas from Combination of Capacitors.
Practice Question
If the space between spheres is filled with a dielectric $\varepsilon_r$, how does the capacitance expression change?
Explore this using deeper theory in Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance.
Related Topics You Should Review
- Energy stored in capacitors
- Dielectric breakdown
- Gauss’s law applications
- Surface charge distribution
- Types of dielectrics and their effects
- Series and parallel capacitor combinations
- Electric field in different geometries
FAQs on Understanding Spherical Capacitance: Concepts and Calculations
5. What factors affect the capacitance of a spherical capacitor?
The capacitance of a spherical capacitor depends on physical and material properties:
- Radii of spheres: Inner (R1) and outer (R2) radius
- Permittivity (ε): Nature of dielectric medium between the spheres
- Distance between spheres: Difference (R2 - R1)
Increasing R1, decreasing (R2 - R1), or using a higher permittivity material increases the capacitance.
6. What is the capacitance of an isolated conducting sphere?
The capacitance of an isolated conducting sphere of radius R in vacuum is:
- C = 4πε0R
This value increases with the radius and is independent of any other objects nearby. This formula is used in many physics exams for direct numericals.
7. What practical applications does spherical capacitance have?
Spherical capacitors have various practical uses in science and engineering:
- Standard capacitor design for calibration
- Electrostatic shielding and storage
- Models for raindrop or planet charge distribution
- Used in radioactivity detection
Understanding these applications helps students connect theory to real-world technology.
9. What is the difference between a parallel plate and a spherical capacitor?
The main differences between parallel plate and spherical capacitors are:
Parallel Plate Capacitor:
- Two flat plates separated by a distance
- Uniform electric field
- Capacitance depends on area and separation
Spherical Capacitor:
- Two concentric spheres
- Radial electric field
- Capacitance depends on radii and separation of spheres
These differences are crucial for CBSE Physics concepts and numerical problems.
10. Why does increasing the radius of a conductor increase its capacitance?
Increasing the radius (R) of a conductor increases capacitance because:
- Larger radius reduces repulsion among stored charges
- Capacitance formula: C = 4πε0R
- Bigger surface can hold more charge at the same potential
This is a key idea for understanding charge storage—an important point for CBSE electrostatics chapters.
























