Master Vedantu's Laws Of Motion Class 11 NCERT Solutions
NCERT for Chapter 4 Laws of Motion Class 11 Solutions by Vedantu, explores the principles governing the motion of objects. This chapter builds on the concepts of force and motion that explains the laws formulated by Sir Isaac Newton.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentThe chapter covers the practical applications of these laws through free-body diagrams, the equilibrium of forces, motion on inclined planes, and circular motion. These concepts are fundamental for solving real-world problems in engineering, design, and everyday activities, making the chapter essential for students pursuing further studies in physics and engineering. Also, understanding these laws is crucial for analysing and predicting the motion of objects in various physical situations. With Vedantu's Class 11 Physics NCERT Solutions, you'll find step-by-step explanations of all the exercises in your textbook, ensuring that you understand the concepts thoroughly.
Master Vedantu's Laws Of Motion Class 11 NCERT Solutions
1. Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on
a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed,
Ans: The net force is zero.
As the speed of the rain drop falling down is constant, its acceleration is zero.
Therefore, from Newton’s second law of motion, the net force acting on the rain drop is zero.
a cork of mass $10g$ floating on water,
Ans: The net force is zero.
It is known that the weight of a cork floating on water acts downward.
The weight of the cork is balanced by buoyant force exerted by the water in the upward direction.
Therefore, no net force acts on the floating cork.
a kite skilfully held stationary in the sky,
Ans: The net force is zero.
The kite is stationary in the sky indicates that it is not moving.
Therefore, from Newton’s first law of motion, the net force acting on the kite is zero.
a car moving with a constant velocity of $30{km}/{h}\;$ on a rough road,
Ans: The net force is zero.
As the car is moving with constant velocity, its acceleration is zero.
Therefore, from Newton’s second law of motion, net force acting on the car is equal to zero.
a high-speed electron in space far from all material objects, and free of electric and magnetic fields.
Ans: The net force is zero.
As the high speed electron is free from the influence of all the fields, no net force acts on the electron.
2. A pebble of mass \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{05kg}\] is thrown vertically upwards. Ignore air resistance and give the direction and magnitude of the net force on the pebble,
during its upward motion,
Ans: It is known that,
Acceleration due to gravity always acts downward irrespective of the direction of motion of an object. The only force that acts on the pebble thrown vertically upward during its upward motion is the gravitational force.
From Newton’s second law of motion: $F=m\times a$
Where,
$F$ is the net force
$m$ is the mass of the pebble, $m=0.05kg$
a is the acceleration due to gravity, $a=g=10{m}/{{{s}^{-2}}}\;$
$\Rightarrow F=0.05\times 10=0.5N$
Therefore, the net force on the pebble is $0.5N$ and this force acts in the downward direction.
during its downward motion,
Ans: The only force that acts on the pebble during its downward motion is the gravitational force.
Therefore, the net force on the pebble in its downward direction is same as in upward direction i.e., $0.5N$ and this force acts in the downward direction.
at the highest point where it is momentarily at rest. Do your answers change if the pebble was thrown at an angle of ${{45}^{\circ }}$ with the horizontal direction?
Ans: When the pebble is thrown at an angle of ${{45}^{\circ }}$with the horizontal, it will have both the horizontal and vertical components of velocity.
At the highest point, only the vertical component of velocity becomes zero. However, the pebble will have the horizontal component of velocity throughout its motion. This component of velocity produces no effect on the net force acting on the pebble.
Therefore, the net force on the pebble is $0.5N$.
3. Neglect air resistance throughout and give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a stone of mass $0.1kg$ ,
just after it is dropped from the window of a stationary train,
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of the stone, \[\mathbf{m}=\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{1kg}\]
Acceleration of the stone, \[\mathbf{a}=g=10{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\]
From Newton’s second law of motion,
The net force acting on the stone is $F=ma=mg$
$\Rightarrow F=0.1\times 10=1N$
It is known that acceleration due to gravity always acts in the downward direction.
Therefore, the magnitude of force is $1N$ and its direction is vertically downward.
just after it is dropped from the window of a train running at a constant velocity of $36{km}/{h}\;$,
Ans: It is given that,
The train is moving with a constant velocity.
Therefore, its acceleration is zero in the direction of its motion, i.e. in the horizontal direction.
Thus, no force is acting on the stone in the horizontal direction.
The net force acting on the stone is because of acceleration due to gravity and it always acts vertically downward.
Therefore, the magnitude of force is $1N$ and its direction is vertically downward.
just after it is dropped from the window of a train accelerating with $1m{{s}^{-2}}$
Ans: It is given that,
The train is accelerating at the rate of $1m{{s}^{-2}}$.
Therefore, the net force acting on the stone is $F'=ma=0.1\times 1=1N$
This force is acting in the horizontal direction. Now, when the stone is dropped, the horizontal force stops acting on the stone. This is because of the fact that the force acting on a body at an instant depends on the situation at that instant and not on earlier situations.
Therefore, the net force acting on the stone is given only by acceleration due to gravity i.e., $F=mg=1N$.
Therefore, the magnitude of force is $1N$ and its direction is vertically downward.
lying on the floor of a train which is accelerating with $1m{{s}^{-2}}$, the stone being at rest relative to the train.
Ans: It is known that,
The weight of the stone is balanced by the normal reaction of the floor. The only acceleration is provided by the horizontal motion of the train.
Acceleration of the train, $a=1m{{s}^{-2}}$
The net force acting on the stone will be in the direction of motion of the train.
Magnitude: $F=ma=0.1\times 1=0.1N$
Therefore, the magnitude of force is $0.1N$ and its direction is in the direction of motion of the train.
4. One end of a string of length $l$ is connected to a particle of mass m and the other to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table. If the particle moves in a circle with speed $v$ the net force on the particle (directed towards the centre) is:
i. $T$,
ii. $T-\frac{m{{v}^{2}}}{l}$ ,
iii. $T+\frac{m{{v}^{2}}}{l}$,
iv. $0$
$T$ is the tension in the string. (Choose the correct alternative).
Ans: (i) $T$
The centripetal force of a particle connected to a string revolving in a circular path around a centre is provided by the tension produced in the string.
Therefore, the net force on the particle is the tension $T$ , i.e.,
$F=T=\frac{m{{v}^{2}}}{l}$
Where $F$ is the net force acting on the particle.
5. A constant retarding force of $50N$ is applied to a body of mass $20kg$ moving initially with a speed of $15m{{s}^{-1}}$ . How long does the body take to stop?
Ans: It is given that,
Retarding force, \[F=50N\]
Mass of the body, $m=20kg$
Initial velocity of the body, \[u=15m/s\]
Final velocity of the body, $v=0$
From Newton’s second law of motion,
The acceleration $(a)$ produced in the body: $F=ma$
$\Rightarrow -50=20\times a$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{-50}{20}=-2.5m{{s}^{-2}}$
From the first equation of motion,
The time $(t)$ taken by the body to come to rest: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow 0=15+(-2.5)t$
$\Rightarrow t=\frac{-15}{-2.5}=6s$
Therefore, the time taken by the body to stop is $6s$.
6. A constant force is acting on a body of mass $3.0kg$ changes its speed from $2.0m{{s}^{-1}}$ to $3.0m{{s}^{-1}}$ in $25s$ . The direction of the motion of the body remains unchanged. What is the magnitude and direction of the force?
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of the body, $m=3kg$
Initial speed of the body, \[u=2m/s\]
Final speed of the body, \[v=3.5m/s\]
Time, $t=25s$
From the first equation of motion,
The acceleration $(a)$ produced in the body: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{v-u}{t}$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{3.5-2}{25}=\frac{1.5}{25}=0.6m{{s}^{-2}}$
From Newton’s second law of motion,
Force, $F=ma$
\[\Rightarrow F=3\times 0.06=0.18N\]
As the application of force does not change the direction of the body, the net force acting on the body is in the direction of its motion.
Therefore, the magnitude of force is $0.18N$ and direction is along the direction of motion.
7. A body of mass $5kg$ is acted upon by two perpendicular forces $8N$ and $6N$. Give the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the body.
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of the body, $m=5kg$
Representation of given data:
Law of Vectors
Resultant of two forces $8N$ and $6N$, $R=\sqrt{{{\left( 8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -6 \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow R=\sqrt{64+36}$
$\Rightarrow R=10N$
Angle made by $R$ with the force of $8N$
$\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{-6}{8} \right)=-{{36.87}^{\circ }}$
The negative sign indicates that $\theta $ is in the clockwise direction with respect to the force of magnitude $8N$.
From Newton’s second law of motion,
The acceleration $(a)$ produced in the body: $F=ma$
$a=\frac{F}{m}=\frac{10}{5}=2m{{s}^{-2}}$
Therefore, the magnitude of acceleration is $2m{{s}^{-2}}$ and direction is ${{37}^{\circ }}$ with a force of $8N$.
8. The driver of a three-wheeler moving with a speed of $36{km}/{h}\;$ sees a child standing in the middle of the road and brings his vehicle to rest in $4.0s$ just in time to save the child. What is the average retarding force on the vehicle? The mass of the three-wheeler is $400kg$ and the mass of the driver is $65kg$.
Ans: It is given that,
Initial speed of the three-wheeler, \[u=36\text{ }km/h\]
Final speed of the three-wheeler, \[v=0m/s\]
Time, $t=4s$
Mass of the three-wheeler, $m=400kg$
Mass of the driver, $m'=65kg$
Total mass of the system, \[M=400+65=465kg\]
From the first law of motion,
The acceleration $(a)$ of the three-wheeler can be calculated from: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{v-u}{t}=\frac{0-10}{4}$
$\Rightarrow a=-2.5{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;$
The negative sign indicates that the velocity of the three-wheeler is decreasing with time.
From Newton’s second law of motion,
The net force acting on the three-wheeler can be calculated as: $F=ma$
$\Rightarrow F=465\times (-2.5)$
$\Rightarrow F=-1162.5N$
The negative sign indicates that the force is acting against the direction of motion of the three-wheeler.
Therefore, the average retarding force on the vehicle is $-1162.5N$.
9. A rocket with a lift-off mass $20,000kg$ is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of $5.0m{{s}^{-2}}$. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
Ans: It is known that,
Mass of the rocket, $m=20,000kg$
Initial acceleration, $a=5m{{s}^{-2}}$
Acceleration due to gravity, $g=10m{{s}^{-2}}$
By using Newton’s second law of motion,
The net force (thrust) acting on the rocket can be written as:
$F-mg=ma$
$\Rightarrow F=m(g+a)$
$\Rightarrow F=20000(10+5)=20000\times 15$
$\Rightarrow F=3\times {{10}^{5}}N$
Therefore, the initial thrust(force) of the blast is $3\times {{10}^{5}}N$.
10. A body of mass \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{40kg}\] moving initially with a constant speed of $10m{{s}^{-1}}$ subject to a constant force of $8.0N$ directed towards the south for $30s$. Take the instant the force is applied to be $t=0$ , the position of the body at that time to be predict its position at \[\mathbf{t}=-\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{s},\text{ }\mathbf{25}\text{ }\mathbf{s},\text{ }\mathbf{100}\text{ }\mathbf{s}\].
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of the body, $m=0.40kg$
Initial speed of the body, \[u=10m/s\] due north
Force acting on the body, $F=-8.0N$
Acceleration produced in the body, $a=\frac{F}{m}$
At $t=0$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{-8}{0.4}=-20m{{s}^{-2}}$
At $t=-5s$
Acceleration, $a'=0$ and $u=10m/s$
$s=ut+\frac{1}{2}a'{{t}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow s=10\times (-5)=-50m$
At $t=25s$
Acceleration, $a=-20m{{s}^{-2}}$ and $u=10m/s$
$s'=ut'+\frac{1}{2}a{{(t')}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow s'=10\times (25)+\frac{1}{2}\times (-20){{(25)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow s'=250+(-6250)$
$\Rightarrow s'=-6000m$
At $t=100s$
For $0\le t\le 30s$, $a=-20m{{s}^{-2}}$ and $u=10m/s$
${{s}_{1}}=ut+\frac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{s}_{1}}=10\times 30+\frac{1}{2}\times (-20)\times {{(30)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{s}_{1}}=300-9000$
$\Rightarrow {{s}_{1}}=8700m$
For $30s\le t\le 100s$
First equation of motion: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow v=10+(-20)\times 30$
$\Rightarrow v=-590m{{s}^{-1}}$
Velocity of body after $30s=-590m/s$
For motion between $30s$ to $100s$ i.e., in $70s$
${{s}_{2}}=vt+\frac{1}{2}a'{{t}^{2}}$
${{s}_{2}}=-590\times 70=-41300m$
Total distance, $s''={{s}_{1}}+{{s}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow s''=-8700+(-41300)=-50000m$
Therefore, the position of the body at $t=-5s$ is $-50m$ at $t=25s$ is $-6000m$ and at $t=100s$ is$-50,000m$.
11. A truck starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at $2.0m{{s}^{-2}}$. At $t=10s$, a stone is dropped by a person standing on the top of the truck ($6m$ high from the ground). Neglect air resistance. What are the
velocity, and
Ans: It is given that,
Initial velocity of the truck, $u=0$ (Initially at rest)
Acceleration, $a=2m{{s}^{-2}}$
Time, $t=10s$
From first equation of motion: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow v=0+2\times 10=20{m}/{s}\;$
Therefore, the final velocity of the truck and the stone is$20{m}/{s}\;$.
At $t=11s$:
The horizontal component $({{v}_{x}})$ of velocity, in the absence of air resistance, remains unchanged, i.e. \[{{v}_{x}}=20m/s\].
The vertical component of velocity $({{v}_{y}})$ of the stone is given by the first equation of motion as:
${{v}_{y}}=u+{{a}_{y}}\delta t$
Where,
$\delta t=11-10=1s$
$a=g=10m/{{s}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{y}}=0+10\times 1=10{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;$
The resultant velocity $(v)$ of the stone is:
Two Velocities of Different Magnitude
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{v_{x}^{2}+v_{y}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{{{20}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}}=\sqrt{400+100}$
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{500}=22.36m/s$
Consider $\theta $ as the angle made by the resultant velocity with the horizontal component of velocity, ${{v}_{x}}$.
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\left( \frac{{{v}_{y}}}{{{v}_{x}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{{{v}_{y}}}{{{v}_{x}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{10}{20} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( 0.5 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{26.57}^{\circ }}$
Therefore, the magnitude of resultant velocity is $22.36{m}/{s}\;$ making an angle of ${{26.57}^{\circ }}$ with the horizontal component of velocity.
acceleration of the stone at $t=11s$?
Ans: When the stone is dropped from the truck, the horizontal force acting on it becomes zero. However, the stone continues to move under the influence of gravity.
Therefore, the acceleration of the stone is $10m{{s}^{-2}}$ and it acts vertically downward.
12. A bob of mass \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{1kg}\] hung from the ceiling of a room by a string $2m$ long is set into oscillation. The speed of the bob at its mean position is $1m{{s}^{-2}}$. What is the trajectory of the bob if the string is cut when the bob is
at one of its extreme positions,
Ans: If the string is cut when the bob is at one of its extremes then the bob will fall vertically on the ground.
Therefore, at the extreme position, the velocity of the bob becomes zero.
at its mean position.
Ans: If the string is cut when the bob is at its mean position then the bob will trace a projectile path having the horizontal components of velocity only.
The direction of this velocity is tangential to the arc formed by the oscillating bob. At the mean position, the velocity of the bob is $1m/s$.
Therefore, it will follow a parabolic path.
13. What would be the readings on the scale of a man of mass \[\mathbf{70kg}\] stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving
upwards with a uniform speed of $10m{{s}^{-1}}$,
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of the man, $m=70kg$
Acceleration, $a=0$(uniform speed)
From Newton’s second law: $R-mg=ma$
Where,
$ma$ is the net force acting on the man.
$\Rightarrow R-70\times 10=0$
$\Rightarrow R=700N$
Reading on the weighing scale$=\frac{700}{g}=\frac{700}{10}=70kg$
Therefore, the mass of the man, $m=70kg$
downwards with a uniform acceleration of $5m{{s}^{-2}}$,
Ans: Acceleration,$a=5{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;$ downward
From Newton’s second law: $R=m(g-a)$
$\Rightarrow R=70\left( 10-5 \right)=70\times 5$
$\Rightarrow R=350N$
Reading on the weighing scale$=\frac{350}{g}=\frac{350}{10}=35kg$
Therefore, the mass of the man, $m=35kg$
upwards with a uniform acceleration of $5m{{s}^{-2}}$.
Ans: Acceleration,$a=5{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;$ upward
From Newton’s second law: $R=m(g+a)$
$\Rightarrow R=70\left( 10+5 \right)=70\times 15$
$\Rightarrow R=1050N$
Reading on the weighing scale$=\frac{1050}{g}=\frac{1050}{10}=105kg$
Therefore, the mass of the man, $m=105kg$
What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity?
Ans: When the lift moves freely under gravity,
Acceleration, $a=g=10m{{s}^{-2}}$
From Newton’s second law: $R=m(g-a)$
$\Rightarrow R=70\left( 10-10 \right)=0$
Reading on the weighing scale$=\frac{0}{g}=\frac{0}{10}=0kg$
Therefore, the man will be in a state of weightlessness.
14. Figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass $4kg$ . Consider one-dimensional motion only and find the
Position- Time Graph for a Particle
force on the particle for $t<0,t>4s$,$0<t<4s$ ?
Ans: For $t<0$ :
From the given graph, it is observed that the position of the particle is coincident with the time axis. It indicates that the displacement of the particle in this time interval is zero.
Therefore, the force acting on the particle is zero.
For $t>4s$ :
From the given graph, it is observed that the position of the particle is parallel to the time axis. It indicates that the particle is at rest at a distance of $3m$ from the origin.
Therefore, no force acts on the particle.
For $0<t<4$ :
From the given position-time graph, it is observed that it has a constant slope. Thus, the acceleration produced in the particle is zero.
Therefore, the force acting on the particle is zero.
impulse at $t=0$ and $t=4s$ ?
Ans: At $t=0$:
\[Impulse=Change\text{ }in\text{ }momentum=mv-mu\]
Mass of the particle, $m=4kg$
Initial velocity of the particle, $u=0$
Final velocity of the particle, $v=\frac{3}{4}m/s$
Impulse $=4\left( \frac{3}{4}-0 \right)=3kgm{{s}^{-1}}$
At $t=4s$:
Initial velocity of the particle, $u=\frac{3}{4}m/s$
Final velocity of the particle, $v=0$
Impulse\[=4\left( 0-\frac{3}{4} \right)=-3kgm{{s}^{-1}}\]
Therefore, the impulse at $t=0$ is $3kgm{{s}^{-1}}$ and at $t=4s$is $-3kgm{{s}^{-1}}$.
15. Two bodies of masses $10kg$ and $20kg$ respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. What is the tension in the string if a horizontal force $F=600N$ is applied along the direction of string to a) A, b) B along the direction of the string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
A,
Ans: It is given that,
Horizontal force, $F=600N$
Mass of body A, ${{m}_{1}}=10kg$
Mass of body B, ${{m}_{2}}=20kg$
Total mass of the system, $m={{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}=30kg$
From Newton’s second law of motion,
The acceleration $(a)$ produced in the system is: $F=ma$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{F}{m}=\frac{600}{30}=20m{{s}^{-2}}$
When force $F$ is applied on body A:
Two Bodies of Masses
The equation of motion can be written as: $F-T=ma$
$\Rightarrow T=F-{{m}_{1}}a$
\[\Rightarrow T=600-10\times 20=400N\]
Therefore, the tension in the string is $400N$.
B along the direction of the string
Ans: When force $F$ is applied on body B:
Two Bodies of Masses
The equation of motion can be written as: $F-T={{m}_{2}}a$
$\Rightarrow T=F-{{m}_{2}}a$
\[\Rightarrow T=600-20\times 20=200N\]
Therefore, the tension in the string is $200N$.
16. Two masses $8kg$ and $12kg$ are connected at the two ends of a light inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
Ans: The given system of two masses and a pulley are represented in the following figure:
Two Bodies of Masses
Smaller mass, ${{m}_{1}}=8kg$
Larger mass, ${{m}_{2}}=12kg$
Tension in the string $=T$
Mass \[{{m}_{2}}\], owing to its weight, moves downward with acceleration $a$, and mass moves ${{m}_{1}}$upward.
Applying Newton’s second law of motion to the system of each mass:
For mass ${{m}_{1}}$:
The equation of motion can be written as: \[T-{{m}_{1}}g=ma\] .......$(1)$
For mass ${{m}_{2}}$:
The equation of motion can be written as: \[{{m}_{2}}g-T={{m}_{2}}a\] ........$(2)$
Adding equations $(1)$ and $(2)$, we get:
$({{m}_{2}}-{{m}_{1}})g=({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})a$
$\Rightarrow a=\left( \frac{{{m}_{2}}-{{m}_{1}}}{{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{1}}} \right)g$ ........$(3)$
$\Rightarrow a=\left( \frac{12-8}{12+8} \right)\times 10=\frac{4}{20}\times 10$
$\Rightarrow a=2m{{s}^{-2}}$
Thus, the acceleration of the masses is $2m{{s}^{-2}}$ . Substituting the value of $a$ in equation $(2)$:
\[\Rightarrow {{m}_{2}}g-T={{m}_{2}}\left( \frac{{{m}_{2}}-{{m}_{1}}}{{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{1}}} \right)g\]
\[\Rightarrow T=\left( {{m}_{2}}-\frac{m_{2}^{2}-{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{1}}} \right)g\]
\[\Rightarrow T=\left( \frac{2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}} \right)g\]
\[\Rightarrow T=\left( \frac{2\times 12\times 8}{12+8} \right)\times 10\]
\[\Rightarrow T=96N\]
Thus, the tension in the string is $96N$.
17. A nucleus is at rest in the laboratory frame of reference. Show that if it disintegrates into two smaller nuclei the products must move in opposite directions.
Ans: Consider $m$, ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ as the respective masses of the parent nucleus and the two daughter nuclei. The parent nucleus is at rest.
Initial momentum of the system (parent nucleus) $=0$
Let ${{v}_{1}}$ and ${{v}_{2}}$ be the respective velocities of the daughter nuclei having masses ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$.
Total linear momentum of the system after disintegration$={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}$
From the law of conservation of momentum:
\[\mathbf{Total}\text{ }\mathbf{initial}\text{ }\mathbf{momentum}=\mathbf{Total}\text{ }\mathbf{final}\text{ }\mathbf{momentum}\]
$\Rightarrow 0={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}=-{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=\frac{-{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}}$
The negative sign indicates that the fragments of the parent nucleus move in directions opposite to each other.
18. Two billiard balls each of mass $0.05kg$ moving in opposite directions with speed $6m{{s}^{-1}}$ collide and rebound with the same speed. What is the impulse imparted to each ball due to the other?
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of each ball$=0.05kg$
Initial velocity of each ball$=6m/s$
Magnitude of the initial momentum of each ball, ${{p}_{i}}=0.3kgm{{s}^{-1}}$
After collision, the balls change their directions of motion without changing the
magnitudes of their velocity.
Final momentum of each ball, ${{p}_{f}}=-0.3kgm{{s}^{-1}}$
Impulse imparted to each ball$=$ Change in the momentum of the system
$\Rightarrow \operatorname{Im}pulse={{p}_{f}}-{{p}_{i}}$
$\Rightarrow \operatorname{Im}pulse=-0.3-0.3=-0.6kgm{{s}^{-1}}$
The negative sign indicates that the impulses imparted to the balls are opposite in direction.
19. A shell of mass \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{020kg}\] is fired by a gun of mass \[\mathbf{100kg}\]. If the muzzle speed of the shell is $80m{{s}^{-1}}$ what is the recoil speed of the gun?
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of the gun, $M=100kg$
Mass of the shell, $m=0.020kg$
Muzzle speed of the shell, $v=80m/s$
Recoil speed of the gun $=V$.
Both the gun and the shell are at rest initially.
Initial momentum of the system$=0$
Final momentum of the system$=mv-MV$
Here, the negative sign appears because the directions of the shell and the gun are opposite to each other.
From the law of conservation of momentum:
\[Final\text{ }momentum=Initial\text{ }momentum\]
$mv-MV=0$
$\Rightarrow V=\frac{mv}{M}$
$\Rightarrow V=\frac{0.020\times 80}{100\times 1000}=0.016m/s$
Therefore, the recoil speed of the gun is $0.016m/s$.
20. A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of ${{45}^{\circ }}$ without changing its initial speed which is equal to $54{km}/{h}\;$ . What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is $0.15kg$)
Ans: The given situation can be represented as:
Deflection of a Ball Hit by a Batsman
Where,
$AO=$ Incident path of the ball
$OB=$ Path followed by the ball after a deflection
$\angle AOB=$ Angle between the incident and deflected paths of the ball$={{45}^{\circ }}$
$\angle AOB=\angle BOP={{22.5}^{\circ }}=\theta $
Initial and final velocities of the ball$=v$
The horizontal component of the initial velocity$=v\cos \theta $ along $RO$
Vertical component of the initial velocity$=v\sin \theta $ along $PO$
The horizontal component of the final velocity$=v\cos \theta $ along $OS$
The vertical component of the final velocity $=v\sin \theta $ along $OP$
The horizontal components of velocities suffer no change. The vertical components of velocities are in opposite directions.
It is known that Impulse imparted to the ball$=$ Change in the linear momentum of the ball.
$\operatorname{Im}pulse=mv\cos \theta -(-mv\cos \theta )=2mv\cos \theta $
It is given that,
Mass of the ball, $m=0.15kg$
Velocity of the ball, $v=54km/h=54\times \frac{5}{18}=15m/s$
Impulse$=2\times 0.15\times 15\cos {{22.5}^{\circ }}=4.16kgm{{s}^{-1}}$
Therefore, impulse imparted to the ball is $4.16kgm{{s}^{-1}}$.
21. A stone of mass $0.25kg$ tied to the end of a string is whirled round in a circle of radius $1.5m$ with a speed of $40rev./\min $ in a horizontal plane. What is the tension in the string? What is the maximum speed with which the stone can be whirled around if the string can withstand a maximum tension of $200N$?
Ans: It is given that,
Mass of the stone, $m=0.25kg$
Radius of the circle, $r=1.5m$
Number of revolution per second, $n=\frac{40}{60}=\frac{2}{3}rps$
Angular velocity, $\omega =\frac{v}{r}=2\pi n$ ........$(1)$
The centripetal force for the stone is provided by the tension $T$ , in the string, i.e., $T={{F}_{Centripetal}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}=mr{{\omega }^{2}}=mr{{\left( 2\pi n \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{Centripetal}}=0.25\times 1.5\times {{\left( 2\times 3.14\times \frac{2}{3} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{Centripetal}}=6.57N$
Maximum tension in the string, ${{T}_{\max }}=200N$
${{T}_{\max }}=\frac{mv_{\max }^{2}}{r}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{\max }}=\sqrt{\frac{{{T}_{\max }}\times r}{m}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{\max }}=\sqrt{\frac{200\times 1.5}{0.25}}$
\[\Rightarrow {{v}_{\max }}=\sqrt{1200}=34.64m/s\]
Thus, the maximum speed of the stone is \[34.64m/s\].
22. If, in Exercise 21, the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks:
the stone moves radially out wards,
the stone flies off tangentially from the instant the string breaks,
the stone flies off at an angle with the tangent whose magnitude depends on the speed of the particle?
Ans: $(ii)$
From the first law of motion, the direction of velocity vector is tangential to the path of the stone at that instant. So, if the string breaks, the stone will move in the direction of the velocity at that instant.
Therefore, the stone will fly off tangentially from the instant the string breaks.
23. Explain why
a horse cannot pull a cart and run in empty space,
Ans: In order to pull a cart, a horse pushes the ground backward with some force. The ground in turn exerts an equal and opposite reaction force upon the feet of the horse.
This reaction force causes the horse to move forward. An empty space is devoid of any such reaction force.
Hence, a horse cannot pull a cart and run in empty space.
passengers are thrown forward from their seats when a speeding bus stops suddenly,
Ans: If a speeding bus stops suddenly, the lower portion of a passenger’s body, which is in contact with the seat, suddenly comes to rest. However, the upper portion tends to remain in motion (as per the first law of motion).
So, the passenger’s upper body is thrown forward in the direction in which the bus was moving.
it is easier to pull a lawn mower than to push it,
Ans: While pulling a lawn mower, a force at an angle $\theta $ is applied on it, as shown in the following figure:
Resolution of Force while Pulling a Lawn Mower
The vertical component of this applied force acts upward. This reduces the effective weight of the mower.
While pushing a lawn mower, a force at an angle $\theta $ is applied on it, as shown in the following figure:
Resolution of Force while pushing a Lawn Mower
In this case, the vertical component of the applied force acts in the direction of the weight of the mower. This increases the effective weight of the mower.
As the effective weight of the lawn mower is lesser in the first case, pulling the lawn mower is easier than pushing it.
From Newton’s second law of motion: $F=ma=m\frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}$ ........$(1)$
Where,
$F=$ Stopping force experienced by the cricketer as he catches the ball
$m=$ Mass of the ball
$t=$ Time of impact of the ball with the hand
From equation $(1)$it can be observed that the impact force is inversely proportional to the impact time, i.e., $F<\frac{1}{\Delta t}$ ........$(2)$
Equation $(2)$ shows that the force experienced by the cricketer decreases if the time of impact increases and vice versa.
Therefore, it is easier to pull a lawn mower than to push it.
a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
Ans: While taking a catch, a cricketer moves his hand backward so as to increase the time of impact $\Delta t$. This in turn results in the decrease in the stopping force, thereby preventing the hands of the cricketer from getting hurt.
Therefore, a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
Laws of Motion Chapter Summary - Class 11 NCERT Solutions
Force
A force is something which changes or tends to change the state of rest or motion of a body. It causes a body to start moving if it is at rest or stop it, if it is in motion, or deflect it from its initial path of motion.
Force is a vector quantity having SI unit Newton (N) and dimension [MLT–2].
Types of Force
There are, basically, four forces, which are commonly encountered in mechanics.
(a) Weight : Weight of an object is the force with which earth attracts it. It is also called the force of gravity or the gravitational force.
(b) Contact Force : When two bodies come in contact, they exert forces on each other that are called contact forces.
(i) Normal Force (N): It is the component of contact force normal to the surface. It measures how strongly the surfaces in contact are pressed together.
(ii) Frictional Force (f) : It is the component of contact force parallel to the surface. It opposes the relative motion (or attempted motion) of the two surfaces in contact.
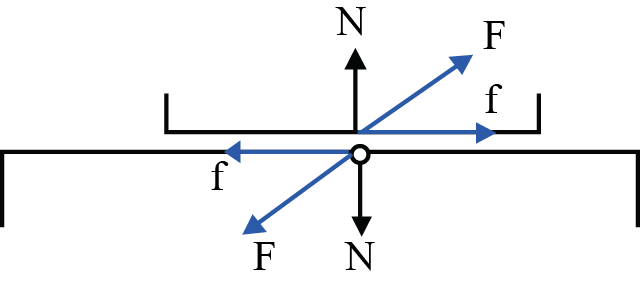
Fig. 5.1
(c) Tension: The force exerted by the ends of a taut string, rope or chain is called the tension. The direction of tension is so as to pull the body while that of normal reaction is to push the body.
(d) Spring Force: Every spring resists any attempt to change its length; the more you alter its length the harder it resists. The force exerted by a spring is given by F = –kx, where x is the change in length and k is the stiffness constant or spring constant (unit Nm–1).
Newton’s Laws of Motion
First Laws of Motion
(a) Everybody continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless it is compelled by a resultant force to change that state
(b) A frame of reference in which Newton’s first law is valid is called an inertial frame, i.e., if a frame of reference is at rest or in uniform motion it is called inertial, otherwise non-inertial.
Second Laws of Motion
(a) This law gives the magnitude of force.
(b) According to second Laws of Motion, the rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on the body, i.e.,
$\vec{F}\alpha \left ( \frac{d\vec{p}}{dt} \right )$
$\vec{F}=K\dfrac{d\vec{p}}{dt}$
Here, the change in momentum takes place in the direction of the applied resultant force. Momentum, $\vec{p}=m\vec{v}$ is a measure of the sum of the motion contained in the body.
Third Laws of Motion
(a) According to this law, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When two bodies A and B exert force on each other, the force by A on B (i.e., action represented by $\vec{F}_{BA}$ ), is always equal and opposite to the force by B on A (i.e., reaction represented $\vec{F}_{BA}$ ). Thus, $\vec{F}_{BA}=-\vec{F}_{BA}$ .
(b) The two forces involved in any interaction between two bodies are called action and reaction. But we cannot say that a particular force is action and the other one is reaction. Action and Reaction force always acts on different bodies.
Applications of Newton’s Laws of Motion
There are two kinds of problems in classical mechanics :
(a) To find unknown forces acting on a body, given the body’s acceleration.
(b) To predict the future motion of a body, given the body’s initial position and velocity and the forces acting on it. For either kind of problem, we use Newton’s second law . The following general strategy is useful for solving such problems :
(i) Draw a simple, neat diagram of the system.
(ii) Isolate the object of interest whose motion is being analysed. Draw a free body diagram for this object, that is, a diagram showing all external forces acting on the object. For systems containing more than one object, draw separate diagrams for each object. Do not include forces that the object exerts on its surroundings.
(iii) Establish convenient coordinate axes for each body and find the components of the forces along these axes. Now, apply Newton’s second law, $\sum \vec{F}=m\vec{a}$ , in component form. Check your dimensions to make sure that all terms have units of force.
(iv) Solve the component equations for the unknowns. Remember that you must have as many independent equations as you have unknowns in order to obtain a complete solution.
(v) It is a good idea to check the predictions of your solutions for extreme values of the variables. You can often detect errors in your results by doing so.
Friction
Friction is an opposing force that comes into play when one body actually moves (slides or rolls) or even tries to move over the surface of another body.
Thus, the force of friction is the force that develops at the surfaces of contact of two bodies and impedes (opposes) their relative motion.
Static Friction, Limiting Friction and Kinetic Friction
The opposing force that comes into play when one body tends to move over the surface of another, but the actual relative motion has yet not started is called Static friction.
Limiting friction is the maximum opposing force that comes into play, when one body is just at the verge of moving over the surface of the other body.
Kinetic friction or dynamic friction is the opposing force that comes into play when one body is actually moving over the surface of another body.
Coefficient of Static Friction
We know that, $f_{ms}\alpha N$ or $f_{ms}=\mu _{s}N$ or $\mu _{s}=\frac{f_{ms}}{N}$ ...(2)
Here, μs is a constant of proportionality and is called the coefficient of static friction. Thus : Coefficient of static friction for any pair of surfaces in contact is equal to the ratio of the limiting friction and the normal reaction. μs, being a pure ratio, has got no units and its value depends upon the nature of the surfaces in contact. Further, μs, is usually less than unity and is never equal to zero.
Since the force of static friction (fs) can have any value from zero to maximum (fms), i.e. fs < fms, eqn. (2) is generalised to fs < μsN
Kinetic Friction
The laws of kinetic friction are exactly the same as those for static friction. Accordingly, the force of kinetic friction is also directly proportional to the normal reaction, i.e.,
$f_{k}\alpha N$ or $f_{k}=\mu _{k}N$ ...(4)
μk is coefficient of kinetic friction. μk < μs.
Circular Motion
It is the movement of particles along the circumference of a circle.
The uniform circular motion is that in which the particle is moving at a constant speed on a circular path.
The non-uniform circular motion is that in which the particles move with variable speed on its circular path.
Variables in Circular Motion
Angular Displacement: It is the angle subtended by the position vector at the centre of the circular path. Angular displacement, $\Delta \theta =\Delta s/r$ where, $\Delta s$ is the arc length and r is the radius
Angular Velocity: The time rate of change of angular displacement $(\Delta \theta )$ is called angular velocity.
Angular velocity, $\omega =\Delta \theta /\Delta t$
Angular velocity is a vector quantity
Relation between linear velocity (v) and angular velocity $(\omega )$ is given by
$v=r\omega $
Angular Acceleration: The rate of change of angular velocity is called angular acceleration.
Angular acceleration,
$\alpha =\lim_{\Delta t\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\Delta \omega }{\Delta t}=\dfrac{d\omega }{dt}=\dfrac{d^{2}\theta }{dt^{2}}$
Its SI unit is rad/s2 and dimensional formula is [T-2]
Acceleration in a circular motion has two components, as given below:
(a) Tangential acceleration is the change in magnitude of linear velocity and act along tangent to the circular path. It is given by:
$\alpha _{T}=r\alpha $
(b) Radial Acceleration is the change in direction of linear velocity and acts along the radius towards the centre of circle. It is given by $\alpha _{r}=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}=\omega ^{2}r$
It is also called centripetal acceleration.
Relation between linear acceleration (a) and angular acceleration $(\alpha )$ ,
$a=r\alpha$ , where r = radius
Relation between angular acceleration $(\alpha )$ and linear velocity (v)
$\alpha =\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$
Centripetal and Centrifugal Force
Centripetal Force: In uniform circular motion, the force acting on the particle along the radius and towards the centre keeps the body moving along the circular path. This force is called centripetal force.
Centrifugal Force: The pseudo force experienced by a particle performing uniform circular motion due to an accelerated frame of reference which is along the radius and directed way from the centre is called centrifugal force.
Motion of a Car on a Plane Circular Road
For motion without skidding
$\dfrac{Mv^{2}max}{r}=\mu M_{g}$
$\Rightarrow v_{max}\sqrt{\mu rg}$
Motion on a Banked Road
Angle of banking $=\theta$
$tan\theta =\dfrac{h}{b}$
Maximum safe speed at the bend $v_{max}=\left [ \dfrac{rg(\mu +tan\theta )}{1-(\mu tan\theta )} \right ]^{1/2}$
If friction is negligible $v_{max}=\sqrt{rg \tan\theta }=\sqrt{\frac{rhg}{b}}$ and $tan\theta =\dfrac{v^{2}_{max}}{rg}$
Motion of Cyclist on a Curve
In equilibrium angle with vertical is $\theta $ , then $tan\theta =\dfrac{v^{2}}{rg}$
Maximum safe speed $=v_{max}=\sqrt{\mu rg}$
Overview of Deleted Syllabus for CBSE Class 11 Physics Laws of Motion
Chapter | Dropped Topics |
Laws of Motion | Exercises 5.24 - 5.40 |
Conclusion
NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Solutions on Laws of Motion provided by Vedantu provide a comprehensive understanding of the principles that govern the motion of objects. The solution cover exercise in the NCERT textbook offers clear explanations and step-by-step methods for solving problems. Important points to focus on include Newton's First Law or the Law of Inertia, Newton's Second Law, Newton's Third Law, the importance of free-body diagrams for visualizing forces, conditions for equilibrium of forces, and the analysis of motion on inclined planes and circular paths. From previous year's question papers, typically around 6–7 questions are asked from this chapter. These questions test students' understanding of theoretical concepts as well as their problem-solving skills.
Other Study Material for CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 4
S. No | Important Links for Chapter 4 Laws of Motion |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 |
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S. No | NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics Chapter-wise List |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | Chapter 6 - Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion Solutions |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 |
CBSE Class 11 Physics Study Materials
S.No. | Study Materials for Class 11 Physics |
|---|---|
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)
1. What are Newton's three laws of motion in Physics?
Newton's laws of motion class 11 include three fundamental principles: First Law (Law of Inertia) states objects at rest stay at rest and moving objects continue moving unless acted upon by force. Second Law relates force, mass, and acceleration (F = ma). Third Law states every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
2. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 help students understand force and acceleration concepts?
NCERT Solutions provide step-by-step explanations of Newton's second law applications, showing detailed calculations for force-mass-acceleration problems with clear algebraic steps and unit conversions.
Students often struggle with vector quantities and applying F = ma in different scenarios like inclined planes or connected masses.
3. What is the law of inertia and how does it apply to everyday situations?
The law of inertia, Newton's first law, explains that objects resist changes in their state of motion - stationary objects tend to stay still while moving objects continue moving in straight lines at constant speed.
This fundamental principle explains countless daily phenomena and forms the basis for understanding all other motion concepts.
4. Can students download laws of motion NCERT PDF solutions for free?
Yes, students can access Free PDF downloads of laws of motion Class 11 NCERT Solutions from Vedantu's website. These comprehensive PDFs include detailed solutions to all in-text questions, exercises, and numerical problems with step-by-step explanations, diagrams, and formula applications for offline study convenience.
5. Why is Newton's third law important in understanding motion?
Newton's third law reveals that forces always occur in pairs - when one object exerts force on another, it experiences equal force in opposite direction. This explains walking (foot pushes ground, ground pushes back), rocket propulsion, and collision dynamics, making it essential for analyzing interactions between objects.
6. How do numerical problems in laws of motion class 11 questions and answers develop problem-solving skills?
Numerical problems combine conceptual understanding with mathematical application, requiring students to identify given data, apply appropriate laws, and solve equations systematically.
These problems test deeper comprehension beyond memorization, preparing students for advanced physics and competitive examinations.
7. What topics are covered in Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions?
Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 question answer coverage includes Newton's three laws with detailed explanations, concept of force and its types, momentum and impulse, applications in daily life scenarios, numerical problems involving force-mass-acceleration relationships, and problem-solving strategies for complex motion situations.
8. How does the concept of momentum relate to Newton's laws of motion?
Momentum (p = mv) connects directly to Newton's second law, which can be expressed as rate of change of momentum equals applied force, providing deeper insight into motion dynamics.
Understanding momentum helps explain collision behavior, conservation principles, and impulse-momentum theorem applications in various scenarios.
Formula: F = dp/dt where p is momentum, relating force to momentum change over time rather than just acceleration.
9. What are common mistakes students make while solving laws of motion questions?
Students frequently confuse mass and weight, forget to consider all forces acting on objects, incorrectly apply Newton's third law to same-object scenarios, neglect vector nature of forces, and rush calculations without proper free body diagrams. NCERT solution class 11 physics chapter 4 addresses these misconceptions systematically.
10. How do laws of motion Class 11 numericals with solutions improve exam preparation?
Solved numericals provide comprehensive practice with step-by-step methodology, covering various difficulty levels from basic applications to complex multi-body systems and real-world scenarios.
Examinations heavily emphasize numerical problem-solving, requiring both conceptual clarity and mathematical precision under time constraints.

























