Exercise-wise Answers and Revision Tips for Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 5 Our Wonderous World Chapter 7 Energy-How Things Work - 2025-26
1. What are the main sources of energy in chapter 7 EVS?
The main sources of energy explained in Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Energy—How Things Work are:
- Sunlight (solar energy)
- Wind energy
- Water energy (hydroelectric power)
- Fuels like coal, petrol, diesel, and LPG
- Food (for living beings)
2. How to answer long questions in class 5 EVS?
For long answer questions in Class 5 EVS Chapter 7, follow a structured and detailed format:
- Begin with an introduction sentence using relevant keywords.
- Explain the concept or process clearly in 2–3 steps.
- Use bullets or numbering for points/facts.
- Include definitions and diagrams wherever required.
- End with a conclusion if needed.
3. Are diagrams or definitions mandatory in answers?
Including diagrams and definitions in Class 5 EVS Chapter 7 answers is important to gain full marks:
- Definitions help in scoring for keyword-based questions.
- Diagrams (like sources of energy) are essential when the question asks for them or when they enhance clarity.
- Label diagrams neatly for extra marks.
4. Where can I download the chapter’s solutions PDF?
You can download the Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Energy—How Things Work NCERT Solutions PDF from trusted educational sites. Look for a free PDF download button on the solutions page for easy offline study and revision.
5. Are NCERT Solutions enough for Class 5 EVS exams?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 EVS provide complete coverage for school exams as they follow the latest CBSE syllabus:
- All intext and back exercise questions are solved stepwise.
- They help you understand key concepts and definitions.
- Practicing these ensures stronger exam confidence and revision.
6. What are the most important topics from this chapter?
The most important topics in Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Energy—How Things Work are:
- Different sources of energy and their uses
- How energy helps things work (daily life examples)
- Conservation of energy and saving energy
- Key definitions and diagrams
7. How to present long answers to match CBSE marking?
To match CBSE marking scheme for long answers in EVS Class 5 Chapter 7:
- Start with a clear definition or introduction.
- Write in stepwise points or ordered steps.
- Highlight keywords and write neatly.
- Add diagrams or examples when asked.
- Stick to the question’s requirements and avoid extra detail.
8. How does this chapter explain energy concepts with real-world examples?
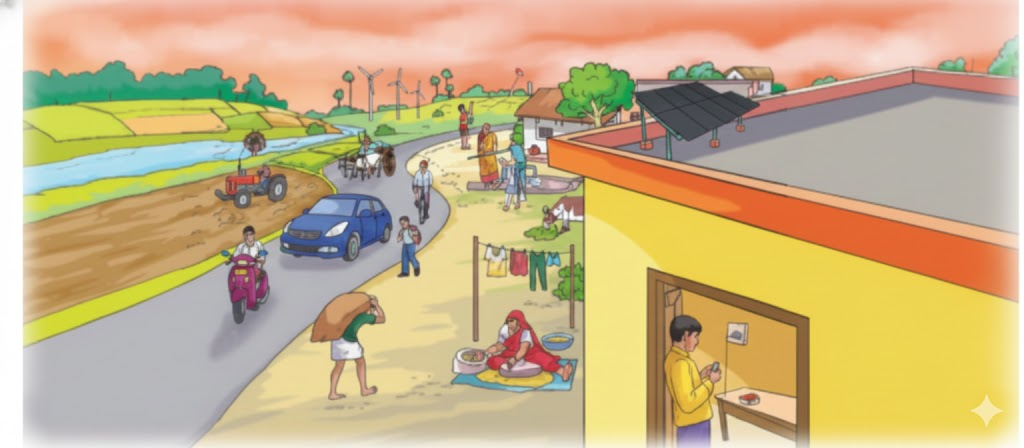
Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 explains energy concepts using real-world situations:
- Shows how energy from food helps humans and animals do work.
- Explains how we use wind, solar, and water energy in daily life (like running fans, lighting bulbs, moving buses, etc.).
- Includes examples and pictures to make learning easy for students.
9. How to learn diagrams and maps for this chapter?
To master diagrams in Class 5 EVS Chapter 7 Energy—How Things Work:
- Practice drawing sources of energy like the sun, windmill, water dam, etc.
- Label all parts neatly using correct terms.
- Follow NCERT textbook diagrams as a model.
- Revise daily and use color for clarity if allowed.
10. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong?
Yes, in CBSE evaluation for Class 5 EVS, examiners often give partial marks if correct steps or key points are mentioned even if the final answer is partially incorrect.
- Write all steps clearly and include relevant keywords.
- Attempt every part of the question for best results.